Networks are formed by switches and routers, which are threaded together with cables. The only working parts on the cable that can go wrong are the connectors, so all of your network monitoring efforts need to be focused on switches and routers.
Here is our list of the six best network device monitoring tools:
- SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor EDITOR’S CHOICE This is the leading network performance monitoring tool and it uses SNMP to discover all network devices, create an asset inventory and automatically draw up a network map. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Datadog Network Device Monitor This cloud-based system is part of a wider platform of system monitoring tools that also includes a traffic monitor.
- Paessler PRTG Network Monitor This package of monitoring systems includes an SNMP system plus options for traffic monitoring. It installs on Windows Server.
- Site24x7 This platform offers a package of tools that provide a mix of system monitoring facilities including network, server, and application performance trackers.
- ManageEngine OpManager This on-premises system monitors networks and servers with SNMP processes at its heart. It runs on Windows Server and Linux.
- Atera This cloud-based system is designed for managed service providers to support clients’ systems and includes SNMP-based network device monitoring.
You can read more about each of these options in the following sections.
Network devices are complicated pieces of devices and many issues can arise that will impair the entire network. Not only do you need to be sure that nothing on the device breaks spontaneously, but you also need to be sure that you are not overloading it with too much traffic volume. Statistics need to be gathered per port and also for the entire device.
Monitoring network devices
Every switch and router has a management console that you can access across the network. This includes screens of statistics on current activity and also notifications on problems. However, you would have to connect to each device in turn and navigate through its console menu to see the data for each device in turn. This just isn’t practical.
Fortunately, there are some very good network device monitoring tools available that do all of the queryings for you and present statistics from every device in one dashboard. Typically, these network monitors will also check for physical problems with all devices, so you can be sure that there are no issues building that is suddenly going to bring the network to a standstill.
The Simple Network Management Protocol
Most of the technology behind remote monitoring for network devices is provided by the Simple Network Monitoring Protocol (SNMP). This protocol is a universal standard that is maintained by the Internet Engineering Taskforce. The system has been adopted by all manufacturers of network devices.
The SNMP system requires a central SNMP Manager and an agent on each device. The agent constantly scans the device and compiles a file-based database of status and statistics. This is called a Management Information Base (MIB).
The SNMP Manager periodically broadcasts a request for reports over the network. The fact that the request is broadcasted means that the SNMP Manager doesn’t need to know exactly what devices are on the network or their addresses. When the device agent hears the request, it immediately sends out its MIB to the return address on the request. If the agent detects a problem, it sends out its MIB with the problem information in it without waiting for a request. This is called a Trap message.
All manufacturers of network devices include an SNMP agent on the equipment as part of the firmware. All that is missing to implement the SNMP system is the manager. Network device monitoring tools perform this role.
The MIB includes information about the device, such as make, model, year of manufacture, and operating system version. It also includes current throughput activity, CPU and memory capacity, and current CPU and memory usage. The MIB contains all of the identifiers assigned to the device and lists all physical ports that are currently in use, together with the identifiers of the device at the other ends of the connection.
Automated network device monitoring
Network device monitoring tools can increase productivity in several ways. First of all, the ability of the tool to centralize reporting on any number of devices saves time that you would otherwise have to spend logging into each device.
The grouping of live performance information also means that information on all devices can be shown on one screen. So, a monitoring tool with an overview on its home page is a big timesaver.
The biggest benefit that you will get from a network device monitoring tool lies with an alerting mechanism. Network device monitors are also known as network performance monitors and they enable thresholds to be placed on any metric that is gathered. For example, you could place a threshold on CPU utilization at 75 percent.
If a threshold is crossed, the monitor will raise an alert. It is possible to set up the system so that it will forward alerts to members of the technical support team by SMS or email. That means that no one needs to sit and watch the dashboard of the monitor waiting for problems to arise. Instead, the team can get on with other tasks, knowing that they will be drawn back to the network device monitoring dashboard by a notification.
Thresholds need to be set at levels that allow the team enough time to take action to lead off disaster. For example, setting the alert threshold on CPU utilization at 100 percent would mean there would already be performance impairment occurring before anyone can do anything about the traffic surge.
SNMP Trap messages also get interpreted into alerts by network device monitors.
Related Post: The Ultimate Network Device Monitoring Guide
The best network device monitoring tools
There are several very good network performance monitors on the market. These all monitor network devices. However, it can take you a long time to read up on all of the available systems. This is why we have drawn up this shortlist.
What do we look for in a network device monitoring tool?
We have examined the market for network performance monitoring systems and analyzed the available packages based on the following requirements.
- A package that can act as an SNMP Manager
- A system to process MIBs into an asset inventory
- Automated network mapping
- Alerts for SNMP Traps
- The facility to generate alerts from performance thresholds
- A free trial or a demo system for a cost-free assessment opportunity
- Value for money represented by a comprehensive tool at a fair price
There are some exciting providers in the network performance monitoring field right now that build on the solid ground of SNMP with innovations that expand the capabilities of the traditional device monitoring task.
1. SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (FREE TRIAL)
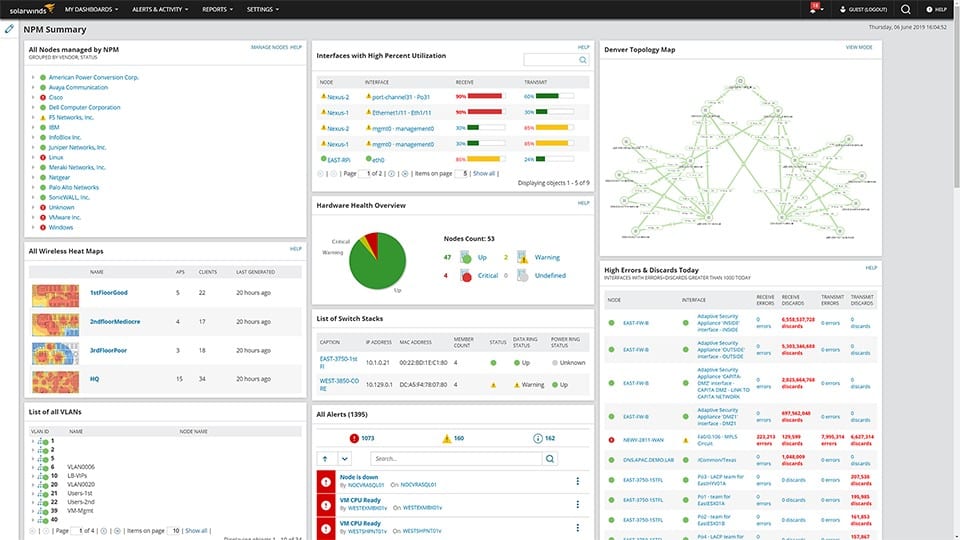
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is a downloadable software package that installs itself and searches through the network to populate its screens. The secret behind all of this automation is the SNMP system. Once the initial network sweep has been completed, you get details about all of your network devices listed in a network inventory and you can switch over to the network map straightaway.
The SNMP cycle provides live network performance data and those polls also update the inventory and the map, so if you add, move, or remove any device, that change is automatically accounted for in the Network Performance Monitor.
Key Features:
- SNMP-based monitor
- Network discovery
- Network asset inventory
- Automatic network topology mapping
- Live performance monitoring
The Home screen for the system provides summaries for all of your devices. This also includes a panel for current alerts. The tool can be calibrated to filter out low-priority alerts, such as warnings and you can also set up forwarding rules to get emails sent out if problems arise. The system can also channel alerts through SolarWinds Help Desk as tickets.
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor also covers wireless networks and has a great wireless signal heatmap feature. SolarWinds produces other tools on the same platform as the Network Performance Monitor and they all interact if you buy several of them.
Pros:
- Stable software with years of sales
- Monitors wireless networks as well as LANs
- Includes procedures for monitoring virtual systems
- Includes alerts as an early warning system
- Offers a customizable dashboard
Cons:
- Doesn’t consolidate the monitoring of multiple networks
The software for SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor runs on Windows Server and you can examine it with a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor is our top pick for a network device monitoring tool because it is a long-established system, which means that it is very stable and bug-free. This is an on-premises package that runs on Windows Server and it can automatically scan, document, and map any network by polling devices for live data through SNMP processes. The Network Performance Monitor will also track the activity on wireless networks and virtual systems.
Get a 30-day FREE Trial: solarwinds.com/network-performance-monitor/registration
Operating System: Windows Server
2. Datadog Network Device Monitor
Datadog Network Device Monitor is a cloud-based service that is part of a wider platform of monitoring tools. There is also a Network Performance Monitoring package available, which is a bandwidth tracking service.
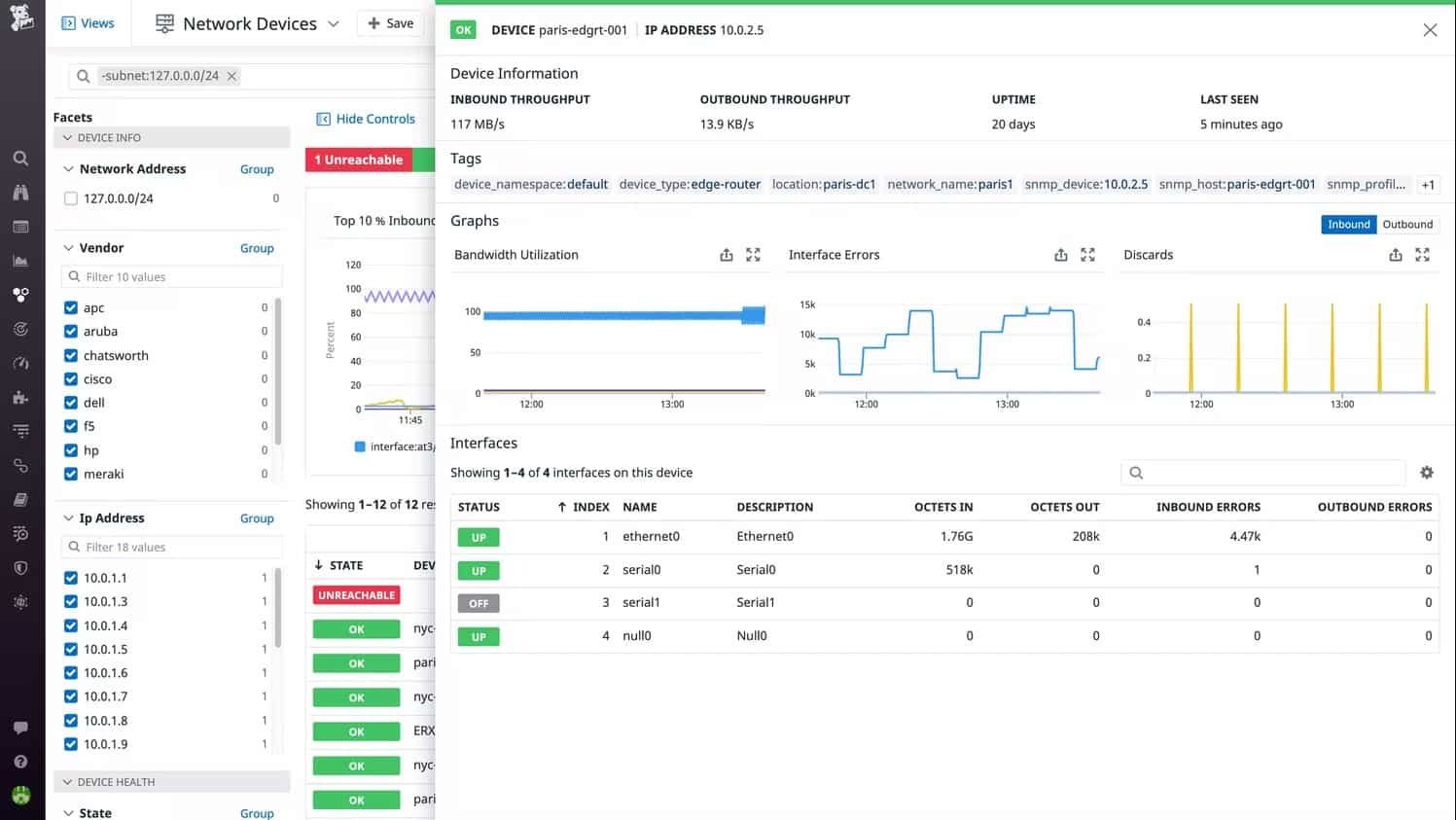
The Network Device Monitor reaches out to any network and it is possible to monitor multiple sites within one account. Each LAN’s data is channeled through an on-site agent, which acts as the SNMP Manager. The service creates an overview for all enrolled networks, which means you can take a single glance at all of your network devices. Network discovery, asset inventory creation, and mapping are all automated.
Key Features:
- Hosted on the cloud
- Can monitoring multiple networks
- Includes live network topology map
- Alerting system
The service also includes a system of thresholds that you can specify on any of the metrics to generate alerts and it also gives you alerts if any Traps are received.
The Network Device Monitor’s screens can be customized and the service also covers wireless networks.
Pros:
- Monitors connections to cloud services
- Tracks on-premises network device performance
- Customizable dashboards
- Will exchange data with other Datadog monitoring modules
Cons:
- Doesn’t include wireless monitoring
You can access the Datadog Network Device Monitor for assessment with a 14-day free trial. Datadog also offers an application performance monitoring system and Web applications synthetic and real user monitoring. All of these are offered on a free trial.
3. Paessler PRTG Network Monitor
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is a customizable package of monitors. Each monitor is called a “sensor” and there are many, many of them in the bundle. You choose which of them to turn on. They cover many aspects of network, server, and application monitoring.
The network monitoring sensors include an SNMP system. This will automatically discover all of your devices and start polling. Among the service in this package are an asset inventory and a dynamically generated network topology map.
Key Features:
- Service dependency mapping
- Free for small networks
- Automatic discovery, inventory creation, and network mapping
If you activate sensors for server and application monitoring as well as the network device monitoring tool, it will create a great dependency map, which is known as the Sunburst View. The package also has sensors for wireless networks, virtual systems, and network traffic monitoring. All of the metrics that the service tracks can have thresholds set on them and the PRTG system will also process SNMP Trap messages.
The PRTG system installs on Windows Server. The pricing of the package depends on the number of sensors that you want to activate. Everyone receives the same software bundle that contains the coding of all sensors. You can activate your purchased number of sensors.
Pros:
- Alerts on performance issues
- Wireless network mapping
- Expandable to server and application monitoring
Cons:
- Doesn’t include any network management functions
If you only want to use 100 sensors, the PRTG system is free to use. You can get a 30-day free trial of PRTG with all sensors active.
4. Site24x7
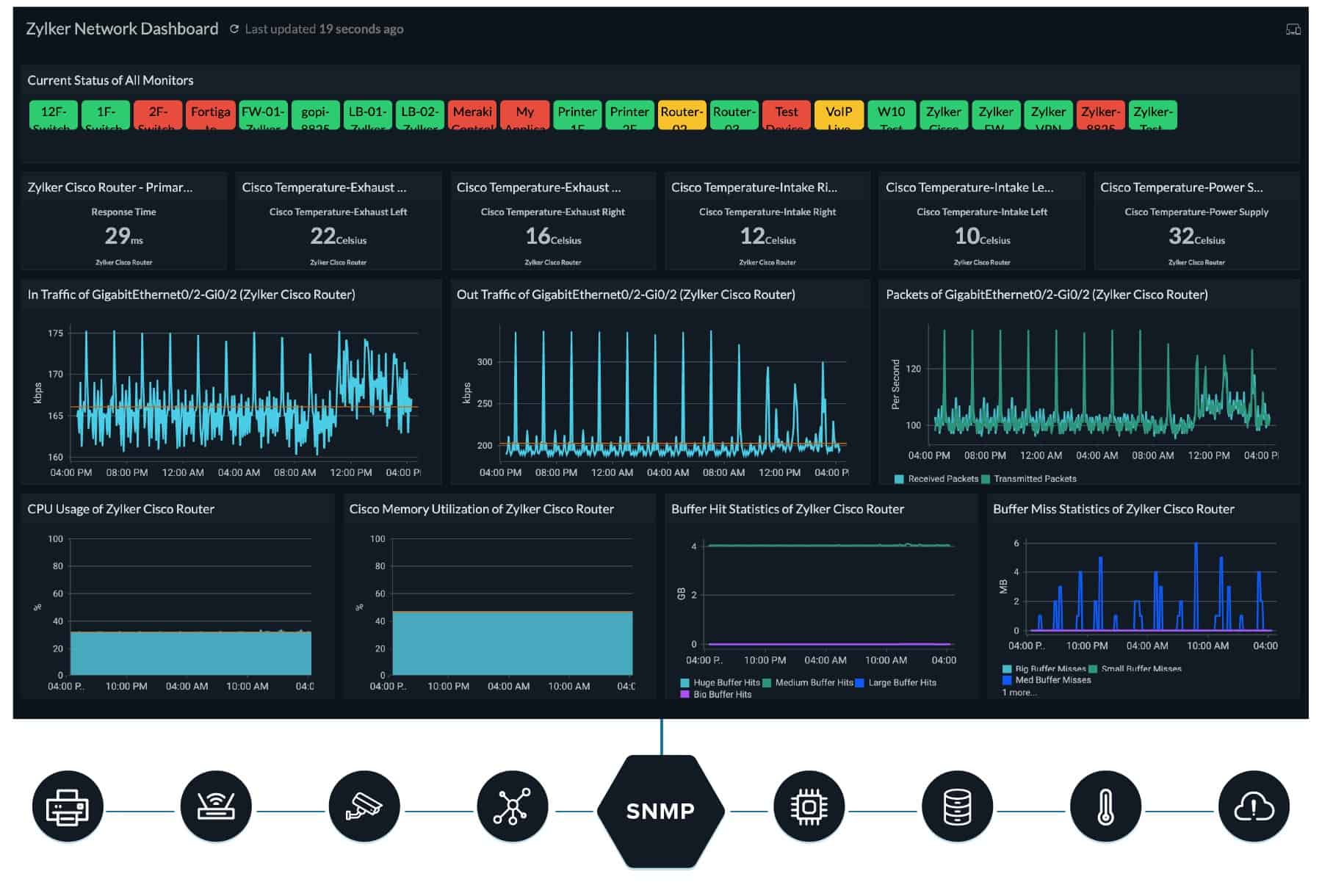 Site24x7 is a SaaS platform that offers a range of system monitoring tools in combinations, such as server, application, and network monitoring services. As this system is hosted in the cloud, it is not limited to monitoring one network. You can monitor multiple sites and centralize their management from one location.
Site24x7 is a SaaS platform that offers a range of system monitoring tools in combinations, such as server, application, and network monitoring services. As this system is hosted in the cloud, it is not limited to monitoring one network. You can monitor multiple sites and centralize their management from one location.
Key Features:
- SNMP-based
- Autodiscovery, asset inventory, and network mapping
- Monitors multiple networks plus cloud resources
The cloud-based system is flexible. The base account gives you a limited number of network credits and if you need to monitor more, you buy add-on credits for more network interfaces. The network monitor gives you an SNMP system, which includes autodiscovery, asset inventory creation, and network mapping. The typical package also offers NetFlow analysis to track traffic flows on each link of the network, examining the load on each switch or router.
Pros:
- Bundled with monitors for servers, applications, and Web systems
- Alerts for unattended monitoring
- Network discovery, asset inventory, and automated mapping
Cons:
- Base packages don’t offer much capacity
Site24x7 is structured in packages that combine network monitoring with server, application, and Web services monitors. You can try the system with a 30-day free trial.
5. ManageEngine OpManager
ManageEngine OpManager is an on-premises package that tracks the performance of network devices and servers. The tool uses SNMP to identify all devices and compile a network asset inventory. The mapping functions of this tool are extensive and offer a range of formats, including floorplan and rack layouts.
The OpManager tool includes an alerting mechanism with notifications that can be sent out by email, SMS, voice call, or Slack post. Alerts can be custom-built on combinations of conditions and it is also possible to set up remediation playbooks for automated responses.
Key Features:
- SNMP-based
- Alerts for SNMP Traps and load problems
- Includes server monitoring
OpManager can monitor virtual systems and wireless networks as well as LANs. The tool includes the ability to examine specific links or play through performance end-to-end between two points on a network.
Pros:
- Automated monitoring with alerts
- Remediation automation
- Options for WAN monitoring
Cons:
- Needs to be hosted
The OpManager system is offered in several editions. One of these is Free but it will only cover three devices. There is also an edition for monitoring WANs and a multi-tenant package for MSPs. The software installs on Windows Server and Linux. You can experience OpManager with a 30-day free trial.
6. Αtera
Atera is designed to support managed service providers. The SaaS platform offers both PSA tools for managing the MSP and RMM tools for use by technicians. This is a multi-tenant service that deploys an agent on each monitored site.
Key Features:
- Remote monitoring and management (RMM)
- Multi-tenant architecture
- Automated monitoring
The Atera network monitor uses SNMP to detect network devices and compile an inventory. It also has a network mapping system. Alerts are included so each technician can cover multiple clients simultaneously and there are also remote access and patch management tools in the bundle.
Pros:
- Monitors the networks of multiple businesses in one account
- Includes alerts
- Network device management tools included
Cons:
- Network discovery costs extra
There are three plans for Atera that make the platform accessible for freelance support operators, medium-sized businesses, and large organizations. You can get the system on a 14-day free trial.
L’article 6 Best Network Device Monitoring Tools est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.
0 Commentaires