Technology has become an inevitable part of our everyday life. In today’s interconnected world, businesses, consumers, and individuals literally depend on technology to carry on with day-to-day activities.
As technology embeds itself into our lives, concerns about cybersecurity continue to rise. Security attacks and breaches have grown exponentially, both in quality and impact potential. When breaches occur, businesses lose customer confidence and ultimately revenue.
In such situations, security testing provides a way for organizations to identify where they are vulnerable in order to take the necessary corrective action to fix the gaps. A growing number of organizations are adopting security testing measures as a way to ensure that their critical applications and infrastructure are shielded from security breaches. The more extensive an organization’s security testing approaches are, the better its overall security posture.
Here is our list of the best security testing solutions:
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager EDITOR’S CHOICE A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution designed to collect and consolidate logs and events from your firewalls, servers, routers, and other devices in your network in real-time.
- Netsparker An easy-to-use automated DAST tool that enables you to scan web applications, websites, and web services for security flaws.
- Acunetix An automated DAST testing tool that audits your web applications by checking for exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Veracode Α cloud-based application security solution company that provides multiple security testing technologies such as DAST, SAST, IAST, SCA, and manual penetration testing, on a single platform.
- Metasploit Α powerful penetration testing and an ethical hacking tool used by attackers and defenders for launching and simulating real-world attacks on a network and executing exploit code.
- RSA Archer Α robust integrated risk management and GRC automation platform designed to help organizations automate their risk management and compliance program.
Security testing is a process intended to reveal flaws in the security mechanisms of an information system. Testing is carried out to determine the level of protection the security controls provide with a view to providing mitigations where necessary. The goal of security testing is to ensure that existing security controls are working effectively. A properly completed security testing should provide documentation outlining any security gaps, as well as measures to address the identified gaps. In this article, we will take a look at security testing, including a review of the best tools that can be used to carry out the task.
Security testing strategies and techniques
Security testing of an environment may take several forms or techniques. Tests may be blind, double-blind, or targeted. However, before carrying out security testing, a written agreement with the management of the target organization is required. This provides legal cover for the tester and ensures that there are no misunderstandings by providing in writing what the tester should—and should not—do. Below are some of the techniques and methodologies used to carry out security testing:
Black-box security testing
Black-box security testing is one in which the assessors do not have any internal knowledge of the target system or network. The goal is to determine the vulnerabilities in a system that are exploitable from outside the network and attempt to exploit them. They are not provided with any network diagrams, IP configurations, or source code that is not publicly available. It is the duty of the assessor to perform all reconnaissance to obtain the sensitive information required to penetrate the system, which places them in the role of the average hacker. This type of testing is the most realistic. However, it also requires a great deal of time to gain insights into inherent weaknesses and develop an attack plan.
Conversely, in software testing, the term is also used to refer to a method of testing the functionality of an application without knowing or examining its internal structures or workings. This testing approach focuses on the input that goes into the software, and the output that is produced. The tester is aware of what the software is supposed to do but is not aware of how it does it. The whole goal is to ensure that the user interface and user inputs and outputs are all working correctly.
White-box security testing
In white-box security testing, assessors are given full knowledge and access to the application, source code, or the network, including diagrams and other documentation. This type of assessment is more precise and targeted, as both internal and external vulnerabilities are evaluated from an “insider” point of view, which is not usually available to typical attackers. The goal is to determine and exploit the vulnerabilities in a system that are exploitable from within and without.
Similarly, in software testing, the term refers to a method of testing the internal structures or workings of an application at the level of the source code. The whole goal is to minimize errors and strengthen security.
Grey-box security testing
Gray-box security testing methodology draws partly from black-box and partly from white-box testing. The purpose of gray-box security testing is to provide a more focused and efficient assessment of a network’s security. The assessor typically has partial knowledge or access to a network’s internals, including design and architecture documentation and some lower-level access credentials to the network. In software testing, the gray-box tester may have partial knowledge of the source code or data structure, as well as the algorithms used.
Now, which of the above security testing methodology is right for your business or project? Well, it all depends on the kind of threat or security concern your organization is trying to address:
- Black-box testing is the most realistic testing method as it addresses concerns posed by an external attacker, but may require sacrificing time and efficiency.
- White-box testing is the most precise and targeted as it addresses concerns posed by insider threats, but requires detailed knowledge of the internal network.
- Gray-box testing seems to be the most effective and efficient as it strives to strike a balance between black-box and white-box testing.
Types of security testing
Different types of security testing are used by security professionals to identify potential threats, measure the likelihood of exploitation, and gauge the overall risks facing the network or application. The actionable insights from these tests are utilized to fix the gaps and minimize security risks. Below are some of the various types of security testing available:
Vulnerability assessment: Vulnerability scanning and assessment identify a broad range of vulnerabilities in a target system. Vulnerability scanning is commonly carried out through a scanning tool that scans a network or system for a list of vulnerabilities such as malware, system misconfiguration, or outdated software. No single tool can find every known vulnerability. A combination of tools may give a better picture of the flaws in your system. Vulnerability testing requires security experts with a deep security background and the highest level of trustworthiness.
The results from a vulnerability scan or assessment are just a “snapshot in time.” As the environment changes, new vulnerabilities can arise. This means that assessments should be performed regularly as changes in the network or system occur. The overall goal of the vulnerability assessment is to:
- Evaluate the true security posture of a network, system, or application.
- Identify, evaluate and prioritize as many vulnerabilities as possible.
- Test how the environment reacts to certain circumstances and attacks, to learn what the known vulnerabilities are, and ways they might be exploited.
Penetration testing
Penetration testing is the process of simulating attacks on a network using a set of procedures and tools that cybercriminals use to possibly bypass the security controls of a system. Penetration testing is usually based on the request of the asset owners, where the pen tester exploits one or more vulnerabilities to prove to the customer that a malicious actor can actually gain access to company resources whether within technologies, people, or processes.
The penetration testing team can have zero, partial or full knowledge of the target network or system before the tests are actually carried out. The main goal of penetration testing is to uncover any weaknesses within an environment, simulate how attackers would exploit those weaknesses in the real world, and measure an organization’s level of resistance to such attacks.
GRC and IT risk assessment
Governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) is the term covering an organization’s overall approach to risk management. It also encompasses having governance policies and procedures in place along with knowing your risk areas and establishing an enterprise-wide compliance program.
A risk assessment is a method of identifying vulnerabilities and threats and the possible impacts to determine where to implement security controls. The goal of risk assessment is to ensure that security is fit-for-purpose, cost-effective, and responsive to perceived threats. Risk analysis helps companies prioritize their risks and the number of resources that should be applied to protecting against those risks. The main objectives of risk analysis are as follows:
- Identify assets and their value to the organization.
- Identify vulnerabilities and threats to those assets.
- Quantify the probability and business impact of these potential threats.
- Provide an economic balance between the impact of the threat and the cost of the countermeasure.
Security auditing
A security audit is a process of reviewing an organization’s security practices against a published standard. It also involves reviewing security audit logs within IT systems to ensure they can effectively support information security goals. Some audits are simply carried out internally for self-reporting purposes, while others may involve the use of a third party or consultant.
An organization may be audited for compliance with security standards such as PCI-DS, ISO/IEC 27002, or HIPAA. The goal is to measure an organization’s level of compliance with a particular security standard.
Application security testing
Apart from testing to evaluate the functionality of an application, application testing is increasingly focusing on finding security flaws that could expose applications to compromise. In application security testing, security attacks and penetration tests are usually carried out to uncover inherent security flaws such as buffer overflows or SQL injection vulnerabilities. When carrying out application security testing, the product interfaces should be hit with unexpected inputs and unusual user activity, denial of service (DoS) situations should be tested, and if the application crashes, appropriate security measures should be put in place to address the identified weaknesses.
There are different automated tools and approaches to software testing. These include:
- Static testing: Static Application Security Testing (SAST) is used to secure applications by reviewing the source code when it’s not running to identify vulnerabilities or evidence of known insecure practices. SAST tools employ a white-box testing strategy that scans the source code of applications and their components to identify potential security flaws. Research has shown that static analysis tools can detect an estimated 50% of existing security vulnerabilities.
- Dynamic testing: Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tool communicates with applications through the front-end in order to identify potential security vulnerabilities. DAST tools do not have access to source codes; rather, they perform actual attacks using the black-box strategy in order to detect vulnerabilities. With dynamic analysis, security checks are performed while actually running or executing the code or application under review. A technique known as fuzzing is used in dynamic tests to submit random, malformed data as inputs to the application to determine if they will crash. Any application that freezes or crashes has failed the fuzz test.
- Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST): IAST combines the best of SAST and DAST. It analyzes code for security vulnerabilities while the app is run by any activity interacting with the application functionality.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): One of the key functions of SCA tools is to identify open source components with known vulnerabilities. A good SCA solution will also tell you whether your code calls the affected library, and suggest a fix where possible.
- Mobile Application Security Testing (MAST): MAST solutions use behavioral analysis to observe the behavior of the applications during runtime and identify actions that could be exploited by an attacker.
Some nonprofit organizations such as Web Application Security Project (OWASP) and Web Application Security Consortium (WASC) provide security guidelines, standardized testing procedures, and best practices for secure software development.
Best security testing tools
With a variety of security testing tools out there, choosing the right one for your business, project, and budget can be challenging. What fits perfectly from a price, feature, and functionality standpoint for one project or business may not fit for another. In this section, we’re going to review some of the best security testing solutions that cover all the various types of security testing discussed above. Hopefully, this will guide you in the process of choosing the right solution for your business or project.
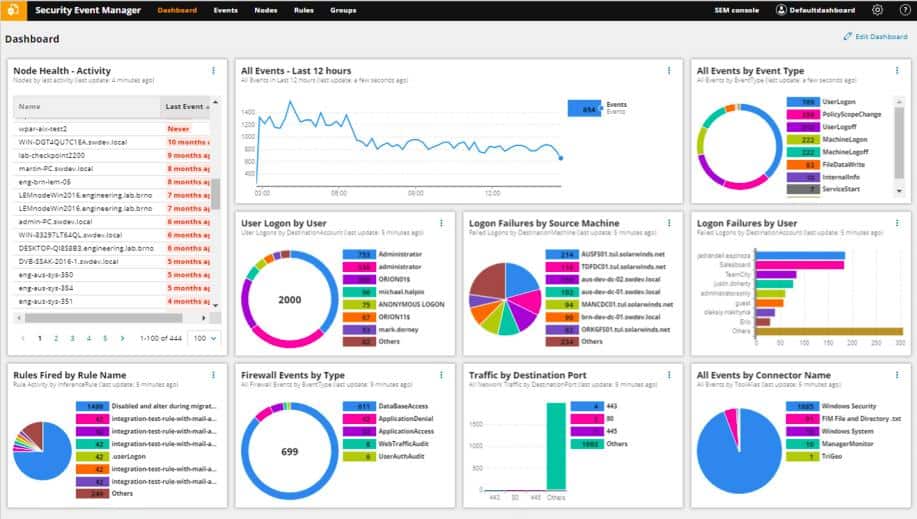
1. SolarWinds Security Event Manager (FREE TRIAL)
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution designed to collect and consolidate logs and events from your firewalls, servers, routers, and other devices in your network in real-time. The solution also comes with lots of pre-built connectors to gather and correlate logs and events from various sources and consolidates them in a central location to support your security auditing, incident response, and compliance reporting efforts.
It not only centralizes logs, but it also provides search features to help you easily visualize and narrow in on the logs you need and even takes automatic action against threats, all in real-time. The platform also offers hundreds of compliance report templates suited to meet the needs of nearly any auditor, helping you demonstrate regulatory compliance. But don’t take my word for it—you can try it out for free yourself, to make sure it’s the right fit for you and your organization before making financial commitments.
SolarWinds Security Event Manager installs on Windows Server and comes with a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution designed to collect and consolidate logs and events from your firewalls, servers, routers, and other devices in your network in real-time.
Start 30-day Free Trial: solarwinds.com/security-event-manager/registration
OS: Windows Server
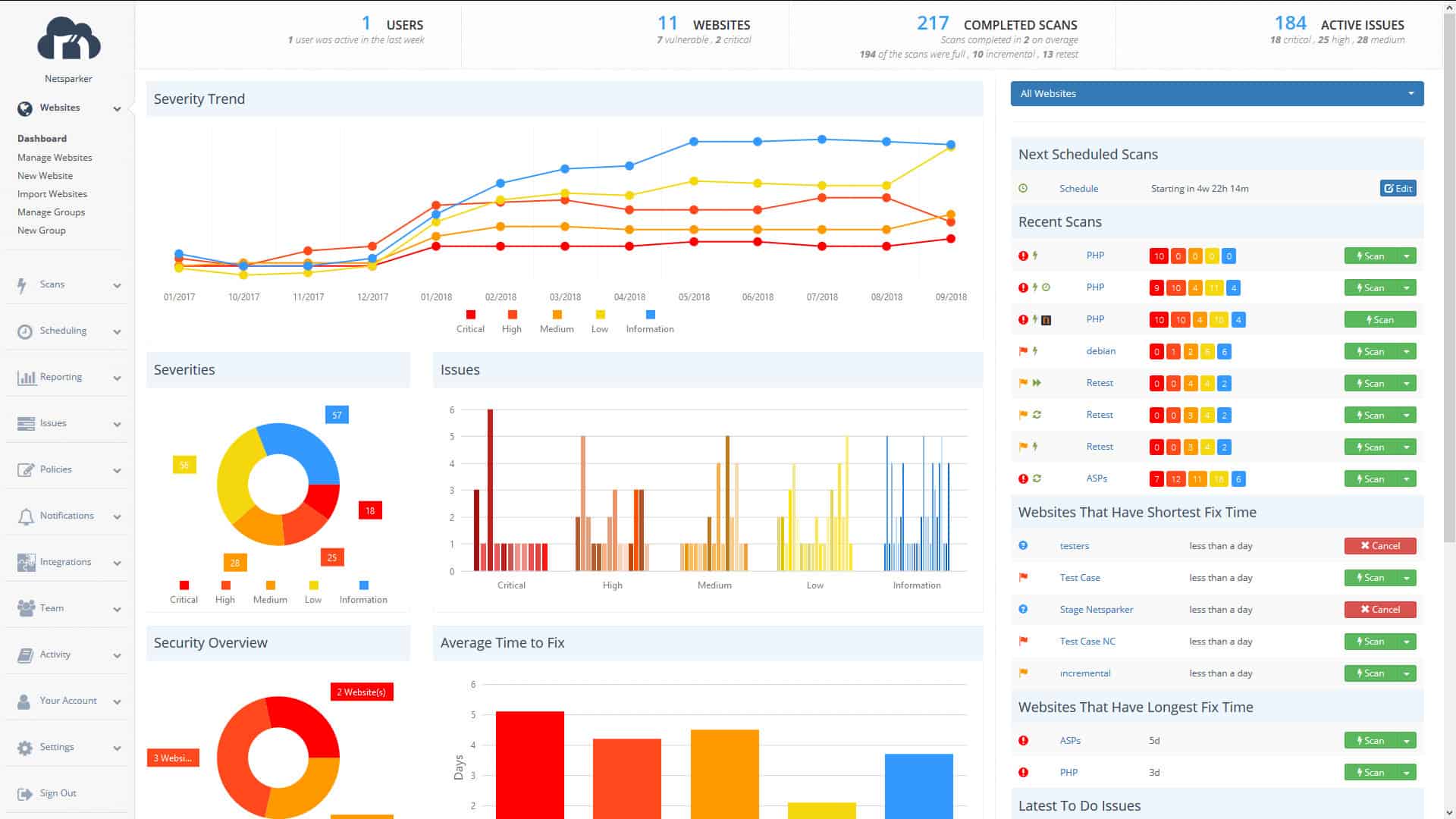
2. Netsparker
Netsparker is an easy-to-use automated DAST tool that enables you to scan web applications, websites, and web services for security flaws. Netsparker is designed for small and medium businesses and doesn’t require you to have deep IT security knowledge to use.
Netsparker also supports Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST); and it uses a heuristic-based approach for detecting vulnerabilities, which makes it easier to identify zero-day vulnerabilities in web applications. Netsparker also uses a proprietary technology called Proof-Based Scanning to safely exploit identified vulnerabilities and automatically create a proof-of-exploit to show that it’s not a false positive. With Proof-Based Scanning technology, you can build DAST into your software development lifecycle (SDLC) to eliminate vulnerabilities before they can reach production.
Some of the vulnerabilities Netsparker scans for are listed in the OWASP Top 10 list of most critical security risks. The product is available in three editions: Standard, Team, and Enterprise as shown in Table 1.0 below. You can try out a free demo to assess its capabilities and make sure it’s the right fit for you and your organization before purchase.
| Features | Standard | Team | Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Designed for | On-premises desktop deployments | For workflows and team collaboration | For scalable, multi-user, cloud, or on-premises deployments |
| Delivery | Desktop Application | Hosted | Hosted or on-Premises |
| Max. no of supported websites | 20 | 50 | 50+ |
User Interface |
Windows Software | Windows Software, web dashboard and mobile support |
Windows Software, web dashboard and mobile support |
| API Access | Command Line | REST API | REST API |
| Proof-Based Scanning Technology (with proof of exploit) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Compliance Reports (Including PCI DSS and OWASP Top 10) |
Yes | Yes | Yes |
Table 1.0 | Comparison of Netsparker product editions
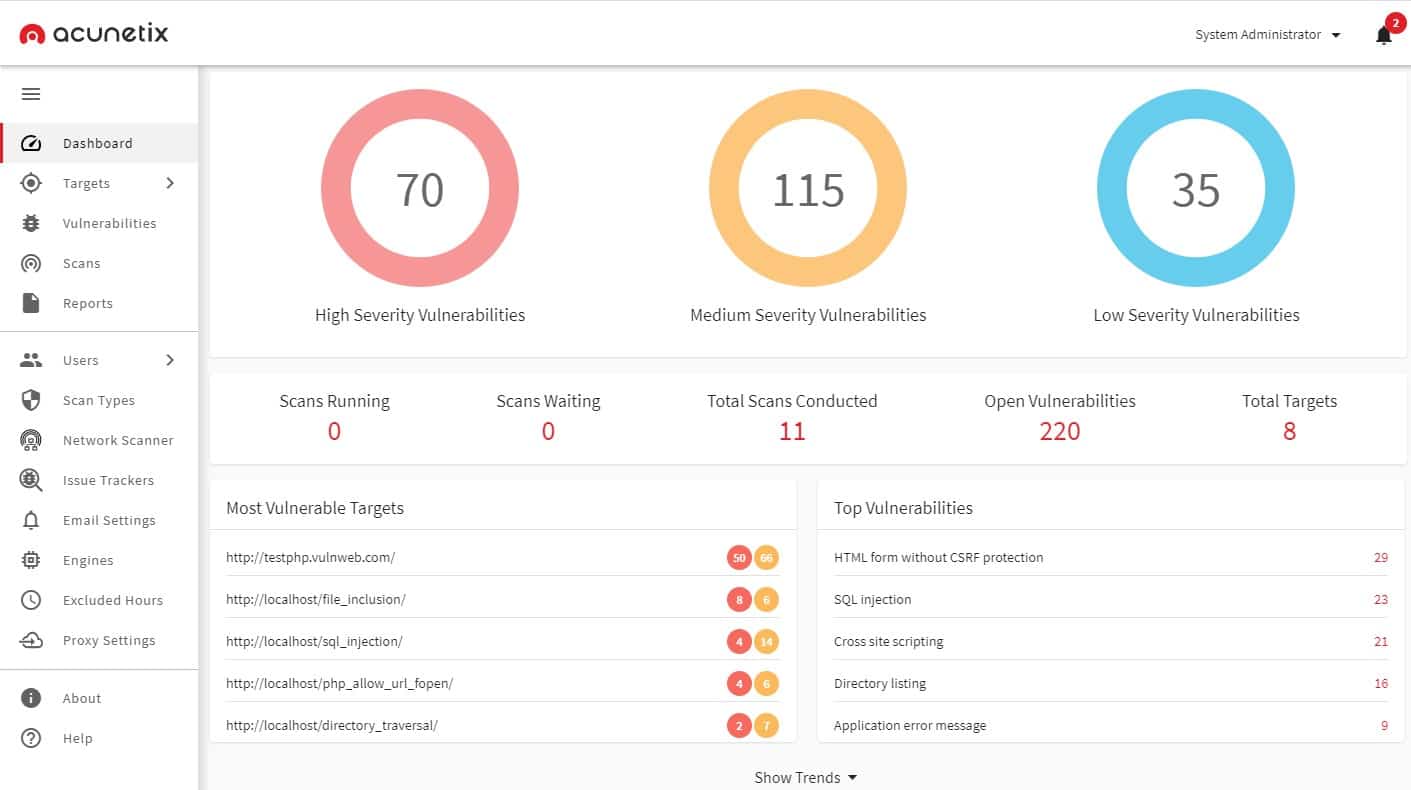
3. Acunetix
Acunetix is an automated DAST testing tool that audits your web applications by checking for exploitable vulnerabilities.
Acunetix is made up of the following key components and features:
- AcuSensor technology: An optional component of Acunetix, which you can use for free with all product licenses. When you install and use AcuSensor, Acunetix becomes an IAST solution (grey-box scanner), not just a DAST scanner (black-box scanner).
- AcuMonitor: A service that allows the scanner to detect out-of-band vulnerabilities. This service is automatically used by out-of-band checks and requires no installation or configuration, only simple registration for on-premises versions.
- DeepScan Technology: Acunetix DeepScan technology enables it to crawl and scan even the most complex website or web application to find all possible entry points.
The product is available in three editions: Standard, Premium, and Acunetix 360 as shown in Table 2.0 below. All three editions can scan for the OWASP Top 10 and are particularly strong at detecting web application security issues such as cross-site scripting, SQL injection, reflected XSS, CSRF attacks, and directory traversal, among others.
| Features | Standard | Premium | Acunetix 360 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable for | Small to medium businesses | ||
| Deployment model | On-premises | ||
| Number of Users | 1 | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Max. Number of Scan Engines | 1 | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| SDLC Integration |
No | Yes | Yes |
Table 2.0 | Comparison of Acunetix product editions
You can try out a free demo to assess its capabilities and make sure it’s the right fit for you and your organization before purchase.
4. Veracode
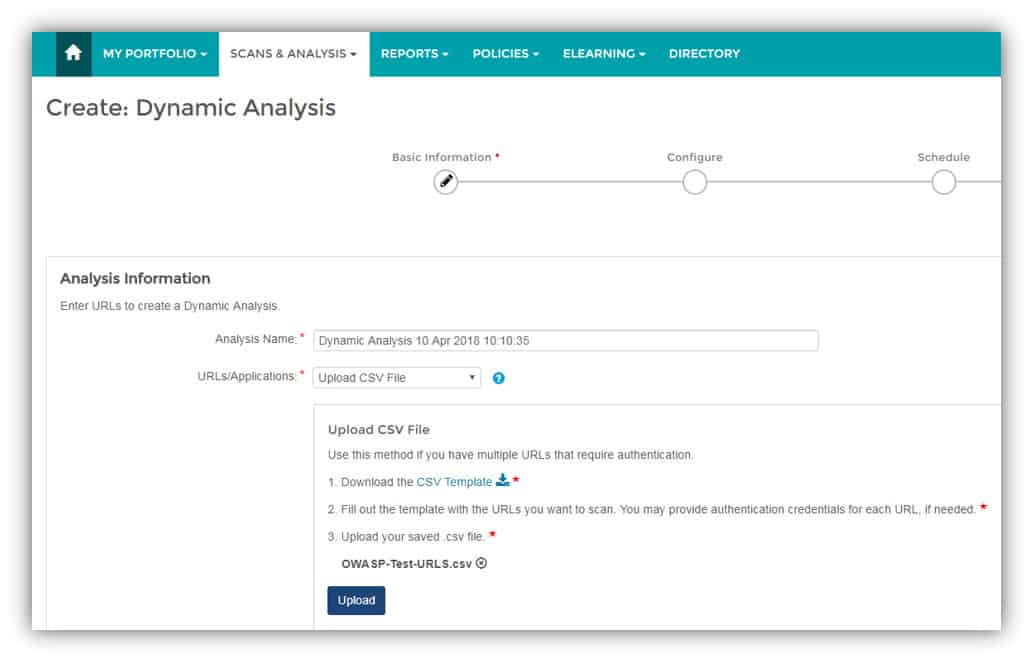
Veracode is a cloud-based application security solution company that provides multiple security testing technologies such as DAST, SAST, IAST, SCA, and manual penetration testing, on a single platform.
Veracode provides DevOps teams with the functionality to gain actionable insights for addressing security vulnerabilities. Integrations exist for GitLab and IDEs such as Eclipse and IntelliJ, etc., helping developers to identify and remediate security vulnerabilities while they code. A personalized solution demo is available for a free trial to enable you to assess its capabilities and make sure it’s the right fit for you and your organization before purchase.
If you are interested in purchasing a Veracode security testing solution, you’ll have to go through a reseller partner in your area.
5. Metasploit
Metasploit is a powerful penetration testing and an ethical hacking tool used by attackers and defenders for launching and simulating real-world attacks on a network and executing exploit code. As of the time of writing, Metasploit has over 2074 exploits, 592 payloads, and a suite of extensively used tools for penetration testing and exploit development. It also includes anti-forensic and evasion tools, as well as hundreds of auxiliary modules that can perform scanning, fuzzing, sniffing, and much more.
Metasploit integrates seamlessly with Nmap, SNMP scanning, Windows patch enumeration, and other reconnaissance tools used to glean information about target systems. The product is available in two editions:
- Metasploit Framework: A free and open-source edition that offers a basic set of features in a command-line-based interface for manual exploitation. This edition is recommended for developers and security researchers. A free download is available.
- Metasploit Pro: An open-core commercial edition that offers a compressive set of advanced features in a GUI-based interface for automated exploitation. This edition is recommended for penetration testers and IT security teams. A free 14-day trial is available
6. RSA Archer
RSA Archer is a robust integrated risk management and GRC automation platform designed to help organizations automate their risk management and compliance program. The solution encompasses audit management, compliance management, IT and security risk management, and much more. The product is mostly targeted at medium to large-scale enterprises.
With Archer IT & Security Risk Management, for example, you can determine which assets are critical to your business, compile a complete picture of security-related risks and their financial impacts, identify and remediate security deficiencies, and establish clear IT risk management best practices.
Some of the key features of RSA Archer Suite include built-in risk taxonomy, integrated industry standards, financial information database, workflow templates, on-demand risk analytics, mathematical simulations, loss tables, and much more. Pricing of this product is available on request. However, it’s important to know that this product is not cheap, which makes it less suitable for SMBs.
Choosing the best security testing tool
As technology embeds itself into our lives, concerns about cybersecurity continue to rise. Security attacks and breaches have grown exponentially, both in quality and impact potential. When breaches occur, businesses lose customer confidence and revenue.
With a variety of security testing tools out there, choosing the right one for your business, project, and budget can be challenging. What fits perfectly from a price, feature, and functionality standpoint for one project or business may not fit for another.
Security testing provides a way for organizations to identify where they are vulnerable in order to take the necessary corrective action to fix the gaps. In this article, we have explored all sources of security testing tools and have identified some very good options with SolarWinds Security Event Manager being the best among them.
L’article Security Testing: Techniques and Tools est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.

0 Commentaires