The modern business environment usually consists of several productivity applications. And depending on the size of the company, there could be a large number of instances, or installations, of each application.
Now, making sure that every single one of these installations is patched and updated could prove to be a daunting task – in some cases, it might even be impossible to accomplish accurately. Fortunately, we have the seven best application patch management tools to make this task a breeze for administrators of even the largest of networks.
Here is our list of the seven best Application Patch Management tools:
- SolarWinds Patch Manager (FREE TRIAL) A corporate-level tool for more extensive infrastructures; it is a powerful tool covering endpoints regardless of location and integrates with Microsoft Update systems for an even more secure patching experience.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus A wholly automated patching tool for almost any device that connects to a network; administrators have complete control over the process and have detailed reports for deep insights.
- NinjaRMM An endpoint patch management tool that is easy to use and yet, lets administrators have total control over patching – right down to selecting and declining individual patches; this makes it the ideal tool for network security, resource conservation, and end-user experience during patching.
- Syxsense A cloud-based tool for patch management of endpoints on any networking environment; health reports that calculate the impact of each vulnerability to get a better sense of the severity of each oversight.
- Atera A patch management tool that gives administrators the flexibility to micro-manage their patch management processes; they can even create custom patch bundles and automation to meet specific requirements or entirely exclude patches they don’t need.
- Kaseya VSA A tool for the administrator who wants to have a powerful patching tool and then much more; it is a suite of administrative tools for remote control, endpoint discovery, network monitoring, etc.
- Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager A tool for automatically evaluating, testing, and deploying the operating system and application patches; this tool can reach endpoints wherever they may be – behind firewalls, remote locations, virtualized – it doesn’t matter, it will find it and patch it.
How do you choose the best application patch manager?
Before we can call it the best in the market, we need to make sure that an application patch management has the following characteristics and features:
- Easy to use – the tool should also be easy to install, configure, and administer.
- Extensive patching capabilities and support should work with a large selection of everyday third-party business and productivity applications.
- Instant vulnerability discovery and identification – constant scanning for instant vulnerability spotting, identifying the issue, and then detecting the correct updates from a well-stocked inventory is expected. Better yet, the system should assess vulnerabilities to offer guidance on which patches to install and in what sequence.
- Automation – any patching tool should automate the process of simultaneously installing multiple patches for numerous applications, even if they are running on various platforms.
- Low bandwidth consumption – patching shouldn’t hog the network bandwidth or even slow it down.
- Agents – another feature that contributes to low bandwidth usage is the use of agents to establish endpoint-to-server connections and communications; optimal polling and connection times make a tool efficient.
- Patch testing and rollback – administrators might need to test the effect of patches before deployment. Also, in case of unforeseen errors, the tool needs a rollback feature to return the endpoints to their prior status.
- Cloud functionalities – patching tools should, at the very least, be cloud-enabled, if not fully cloud-based.
- Cross-platform support – a good tool that can manage all endpoints, including cross-platform support for Windows, macOS, and the many flavors of Linux.
- Insightful reporting – reports are a critical feature in application patch management tools because that is the only way administrators can have insights into compliance while keeping an eye on the overall health.
- Great price – a good solution shouldn’t be expensive, and a cheap (or free) one shouldn’t be assumed to be inefficient; the trick is in finding the optimal solution in terms of price and performance.
The Seven Best Application Patch Management Tools
Ok, let’s jump straight into it; here are the seven best application patch management tools.
1. SolarWinds Patch Manager (FREE TRIAL)
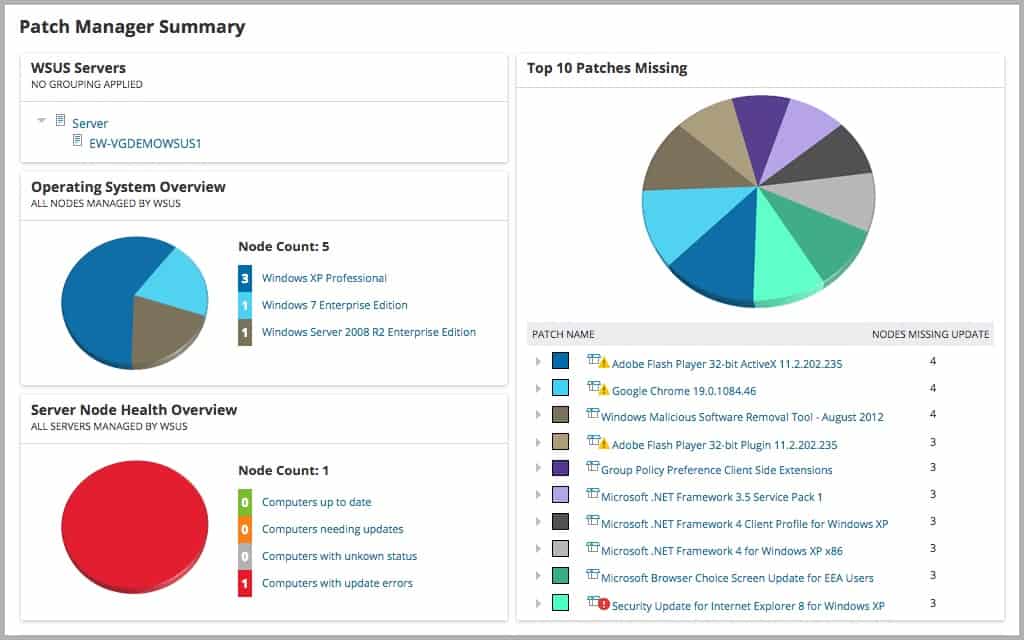
SolarWinds Patch Manager is a patch management solution developed by leaders in the application and server monitoring and management tools market. It is an on-premise patch management software solution designed to quickly and efficiently address software vulnerabilities.
Looking at some of its features, we find:
- It simplifies many of the steps in the patch management process, including the research, scheduling, deployment, and reporting on patching and vulnerability issues.
- Administrators have a central dashboard from which they can stay on top of security updates, track patch versions, and even be notified of failed patch deployments, thus avoiding security issues before they occur.
- It integrates well with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) and the Microsoft update agent to update Windows patches automatically, allowing it to automatically update Windows patches.
- It also has software deployment tools for Windows to extend the System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM).
- Of course, Patch Manager also helps with the deployment of updates for third-party applications; it offers pre-built, tested, and automatically delivered packages for commonly used applications like Adobe, Google, and Oracle
- Administrators can create custom patching schedules to meet requirements that are unique to their networks.
- They can even get a heads up to proactively identify servers and workstations that need to be patched, after which the tool allows them to build patch deployment packages to meet these specific demands.
- These customizations include control and scheduling of software patching for endpoints based on their operating systems, IP ranges, custom device groupings – or even individual device selections.
- This is an ideal solution for businesses with a more extensive installation containing thousands of endpoints. In addition, it can handle the deployment of large numbers of devices – custom or otherwise – with ease.
- Apart from patching customizations, administrators can also specify reboot preferences, force updates, or define specific group updates overriding the end users’ preferences.
- In the meantime, administrators keep track of the whole process via a patch status dashboard and confirm compliance later through various insightful reports that Patch Manager offers.
- These reports are fully customizable and can be sorted, filtered, scheduled, exported, and emailed – enhancing the administrators’ ability to stay on top of their network’s security.
Try SolarWinds Patch Manager with a fully functional 30-day free trial.
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus
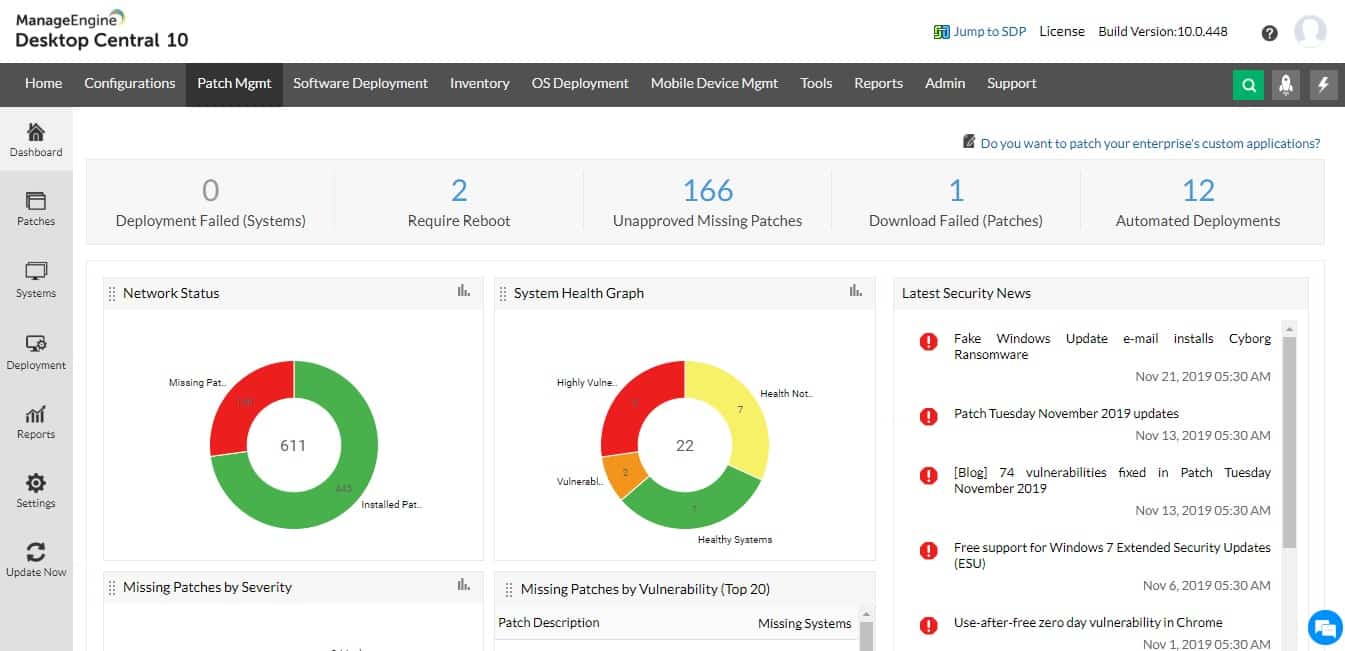
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is an application patch management tool available as an on-premises or cloud solution. It supports Windows, Mac, and Linux operating systems.
The tool supports automated patch deployment of over 900 updates for over 500 third-party applications that include Adobe, Java, WinRAR, and more.
Other features include:
- Patch Manager Plus automatically spots which applications need to be patched, and the process of acquiring third-party application patches is also completely automated and controlled from a central point.
- Administrators can also spot missing patches by manually scanning the endpoints; they can then test available deployable patches to ensure they resolve the vulnerabilities without causing further complications.
- They can also track the availability of new patches and have the flexibility of synchronizing patches as per preferred schedules or perform selective deployment of sensitive patches depending on their compliance needs – the tool offers complete flexibility.
- It can cover almost any device type on a network: desktops, laptops, servers, roaming devices, and virtual machines (VMs).
- All patch deployment processes can be monitored and controlled using robust audits and reports.
- An essential feature in this tool is the ability for administrators to decline patches should they be found to be disruptive until the software or hardware vendors have come up with a better patch.
Try the cloud or on-premise version of ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE for 30 days.
3. NinjaRMM
NinjaRMM is a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tool that gives administrators complete visibility and control over end-users applications running on managed endpoints. In addition, it has a third-party patching engine that can keep over 135 typical applications up-to-date – without the users’ input being required.
The tool offers more:
- NinjaRMM makes it easy to monitor and control application-related vulnerabilities with its detailed software inventory and built-in tools for deployment, removal, and blacklisting applications.
- This tool covers the entire IT infrastructure and keeps them secure and updated using patch deployments for devices running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems and the applications that run on them.
- NinjaRMM supports the patching of many of the most commonly used applications like Microsoft Edge, MS Office, Office 365, and much more.
- The patches can be sent out to endpoints singularly, in groups, or broadcasted across the whole infrastructure.
- A central dashboard gives insight into the patch status of all endpoints and displays details like successfully deployed patches, those that are still pending, as well as those that have failed to install correctly.
- End-users don’t need to be joined to the domain, be on the company network or use a VPN for their endpoints to be patched; what’s even better is that there is no complex and expensive patching server to set up and maintain – a win-win solution for both administrators and the end-users user experience (UX).
- The tool has aesthetic and insightful reports on patch compliance status, security vulnerabilities, and much more – accessible at a click of a button – and which can be used as reference or proof of compliance.
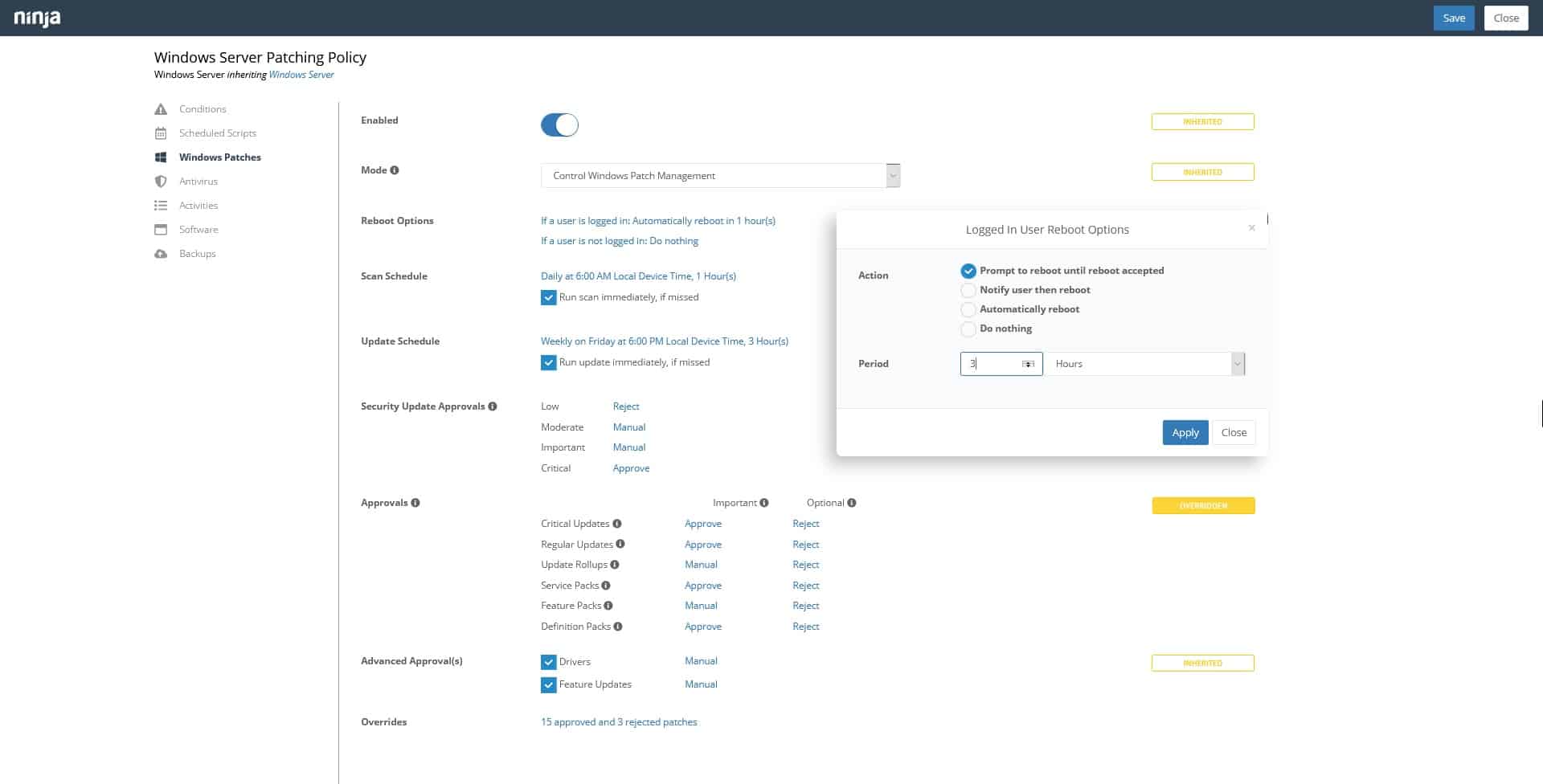
- It has automatic patch approval settings for each patch type and criticality and can be configured for complete control over scanning times, updating schedules, reboot options, and more; administrators also have complete control over how each endpoint is patched with the capability of patch identification, approval, and deployment schedules.
- Administrators can use patch policies to optimize and automate the deployment process across the infrastructure while also using manual, ad-hoc management in case there are individual critical updates that need to be deployed immediately.
Try NinjaRMM for FREE.
4. Syxsense
Syxsense is a tool with IT management, security vulnerability scanning, and patch management capabilities – all packed into one powerful suite. In addition, it is a cloud-based tool that is hosted in Microsoft Azure. This makes it the ideal tool for cloud-based or hybrid networking environments, but it would still be a practical application patch management tool even if used on LANs.
Here are some more features:
- Syxsense monitors desktops, laptops, and servers running Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems; the endpoints’ location doesn’t matter – they can be roaming devices that are not connected to the administrators’ domain all be patched and updated.
- Apart from updating the operating systems, this tool can automatically deploy patches for third-party applications like Adobe, Java, and Chrome; it can also check for hotfixes, bug fixes, and any other patches or updates that application vendors send out.
- Administrators can set the patch deployment times for when they won’t interfere with productivity hours; they can also be scheduled for standing times – think Microsoft’s Patch Tuesdays – when they are sure there will be critical updates being sent out.
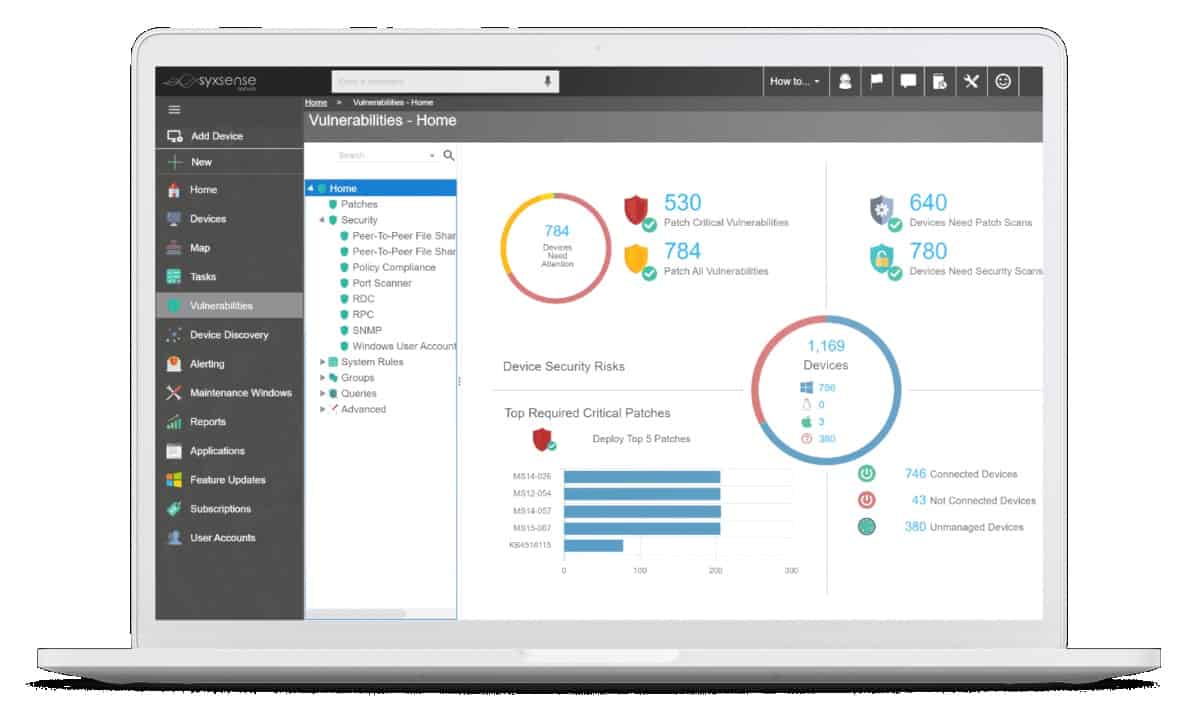
- The tool has a device health monitor that shows where immediate patching is required or if any patches are missing, for immediate action to be taken; the impact of these vulnerabilities is calculated using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to give a better indication of the severity of the oversights.
- The tool has a list of detailed reporting tools that give insights into the whole patching process and can be further adapted depending on custom requirements through parameters and filtering.
- The resulting reports can be used as executive overviews or finely detailed audits; examples of such reports are those having titles like Security Risk Assessment, Most Vulnerable Devices, and Task Summary – all of which can be scheduled for automatic receipt, exported for further analysis or used as proof of compliance to HIPAA, SOX or PCI.
Try Syxsense Manage FREE for 14 days.
5. Atera
Atera’s Patch Management Software is a tool that gives complete control of patching across entire networks. It offers automatic patching of endpoint operating systems, applications, and hardware – all of which can be overseen from a central location with every agent being tracked to ensure continuous watertight security.
Looking at some features:
- Atera can be configured to meet custom preferences for patching of endpoints that, themselves, handle critical driver updates; it has automatic patch management for Windows and macOS operating systems via integrations with Chocolatey and Homebrew.
- It can patch most of the common business productivity software solutions found in every office like Zoom, Java, Dropbox, and Chrome.
- It offers flexibility by allowing administrators to create software bundles or custom automation to meet their specific endpoint requirements or exclude sure patches they deem unnecessary, for example.
- Even better, Atera offers a Shared Script Library with scripts that can be cloned and automatically added to automation profiles; these scripts are shared by the user community and are checked for quality by the in-house team allowing for a secure and customized patching experience.
- Insightful and shareable reports are also part of Atera’s features that allow for better control and oversight of the patching processes; examples include a Patch Search and Deploy report for Microsoft KBs that would enable installing patches directly from the report.
Try Atera FREE for 14 days.
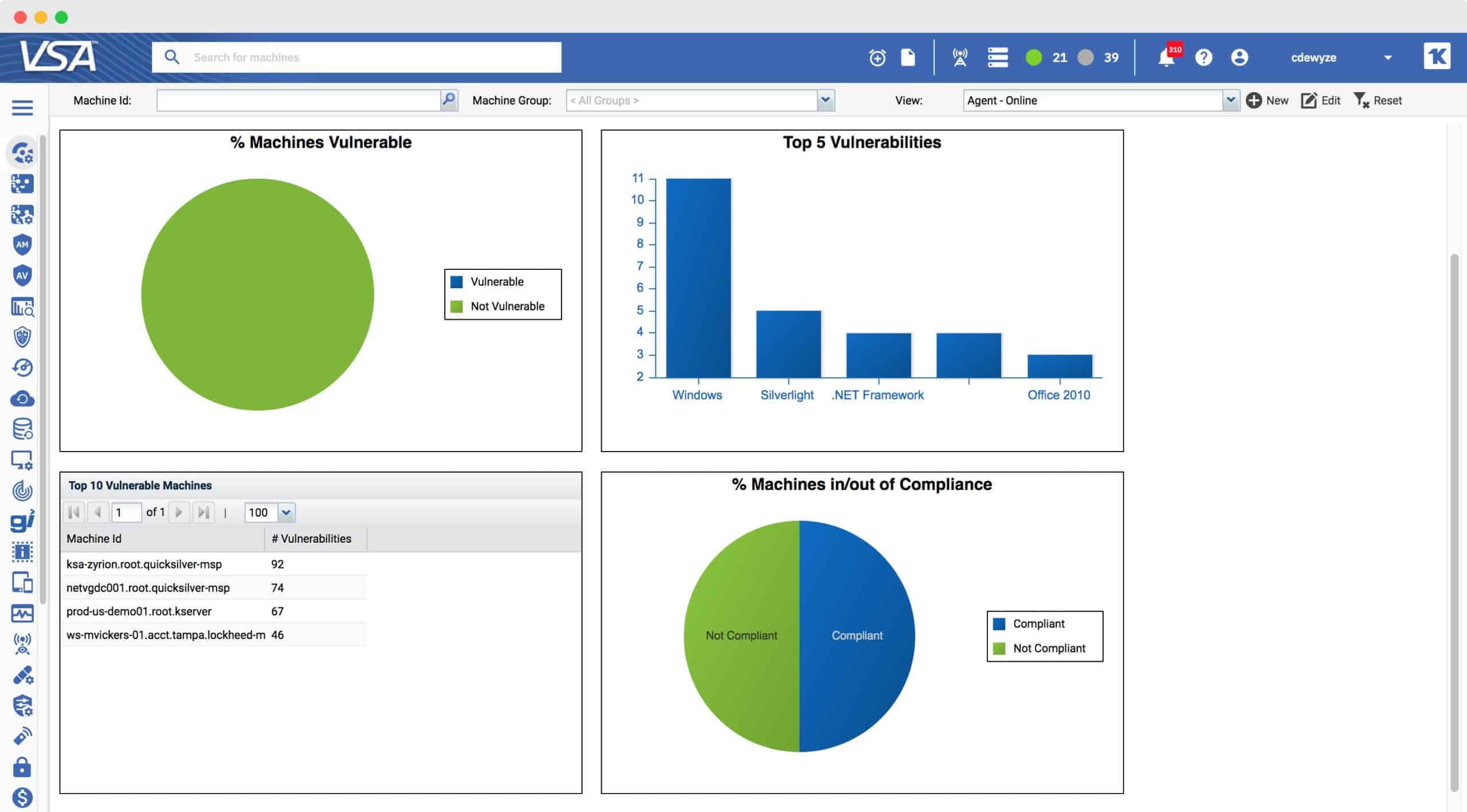
6. Kaseya VSA
With the Kaseya VSA Patch Management Software, we get a suite of tools for remote control, IT automation, network monitoring, endpoint discovery and inventory, and application patch management. It is used to install, deploy, and update software across endpoints. But, that’s not all; it also has various add-ons for office productivity and data security features.
And there’s even more:
- With Kaseya VSA, administrators have complete control over their patching processes, including running scripts to exclude patches that may have issues or cause conflicts when installed.
- The tool intelligently manages software for Windows, macOS, and the third-party applications that run on them.
- A central dashboard allows for central monitoring of the patching process and gives insights into vulnerabilities by gauging the health status of the entire infrastructure; administrators can also easily install, uninstall, update, repair, and modify software from there.
- On the other hand, Patch reports can be easily configured to monitor compliance across the network or spot operating systems, third-party applications, and endpoints that need immediate remedial actions.
- Kaseya helps avoid any complications during patch deployments with the help of its native and easy-to-use policy profiles for managing patch approval, scheduling, and installation; administrators can use the VSA agent endpoint fabric to optimize the delivery of installation packages further and avoid the need for a centralized File Share or LAN Cache.
- Administrators can schedule their network scanning and analysis for after-hours and also use Blackout Windows to completely stop processing during peak hours – both of which ensure a more excellent UX on the endpoints.
- They can also override default patching policies by skipping specific patches, KBs, and updates – from being sent out to a single endpoint, a subnet of them, or the network as a whole.
Try Kaseya VSA FREE for 14 days.
7. Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager is a tool for automatically evaluating, testing, and deploying the operating system and application patches. It also manages patch deployment for third-party applications.
Looking at more features:
- Ivanti can patch physical or virtual Windows servers and workstations and Linux, UNIX, and macOS devices; it will also patch the third-party apps running on them – it doesn’t matter how heterogeneous the network is.
- It offers remote patching that extends to endpoints located beyond the network, regardless of where they are – they could be behind firewalls, roaming, at remote sites, or even asleep – Ivanti can reach them all.
- This reach also extends to virtual machines – it can patch both online and offline VMs and hypervisors.
- Ivanti supports application patching of the most vulnerable apps like Adobe Acrobat Flash, Java, and Internet browsers.
- A centralized console makes it easy to perform all tasks – managing updates and patching of native and third-party applications and securing and managing endpoints – everything is controlled from a Microsoft Endpoint Manager (MEM) console.
- The tool allows for the packing and pre-caching of multi-application patches – which can also be tested beforehand – for quick deployments with zero downtimes; alternatively, patch rollouts can be done in stages to minimize the impact performance of networks and endpoints.
- Administrators can take advantage of insightful, consolidated, and detailed reports on security and vulnerabilities. These reports can serve as proof of compliance or serve as audits for quick actions against critical vulnerabilities.
- Finally, administrators can also interact directly with the endpoints and send out commands for Wake on WAN (WoW), device booting or rebooting, exclusions from patching, and scheduling after-hours patching times.
Try Ivanti for FREE.
would like to hear your thoughts on them. Perhaps, you have a patch management tool you think needs to be on the list. Either way, please let us know; leave a comment below.
L’article 7 Best Application Patch Management Tools for 2021 est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.


0 Commentaires