
Individuals and organizations in the US need to be warier than ever about cyber crime and its impacts. Threats such as phishing schemes, ransomware attacks, and various types of fraud all feature heavily in the US cyber crime landscape. Advancing technology and increased awareness mean that users are stepping up their cyber security practices, but it’s tough to stay ahead of determined cyber criminals.
Below, we paint a picture of what’s happening in the world of US cyber security with statistics from the latest studies and reports:
1. Almost 89.7% of US organizations saw at least one successful attack over a one-year timeframe
The Cyberthreat Defense Report (CDR) by CyberEdge Group offers lots of information about cyber attacks in various regions. It tells us that in the US, 89.7 percent of organizations have been compromised by a cyber attack within a 12-month period. That is a massive 6.7 percent increase over 2020.
Five countries in the study saw a higher portion of impacted organizations: Mexico (90.6 percent), Spain (89.8 percent), Germany (91.5 percent), Colombia (93.9 percent), and China (91.5 percent).
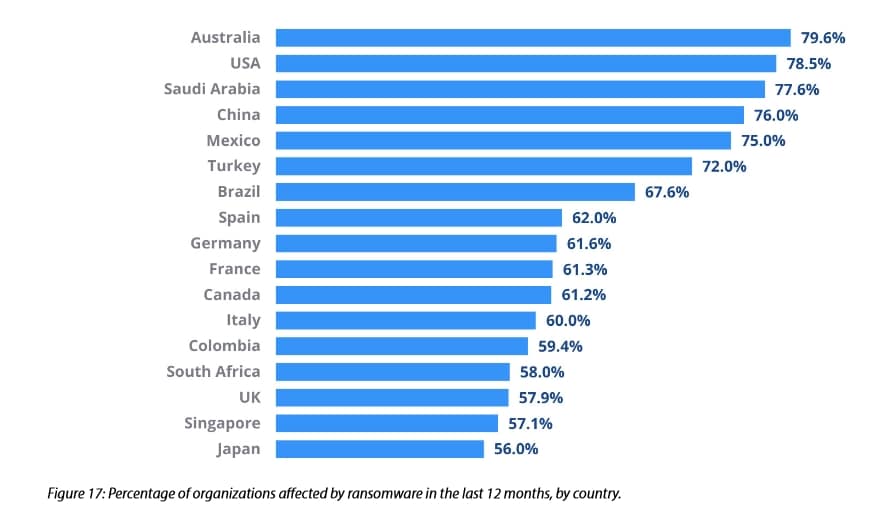
2. Ransomware affected almost 78.5% of US organizations within a year
The CyberEdge report also reveals how many companies were hit by ransomware. It discovered 78.5 percent of American organizations dealt with a ransomware attack in 2020. The US was the second most impacted country behind Australia.
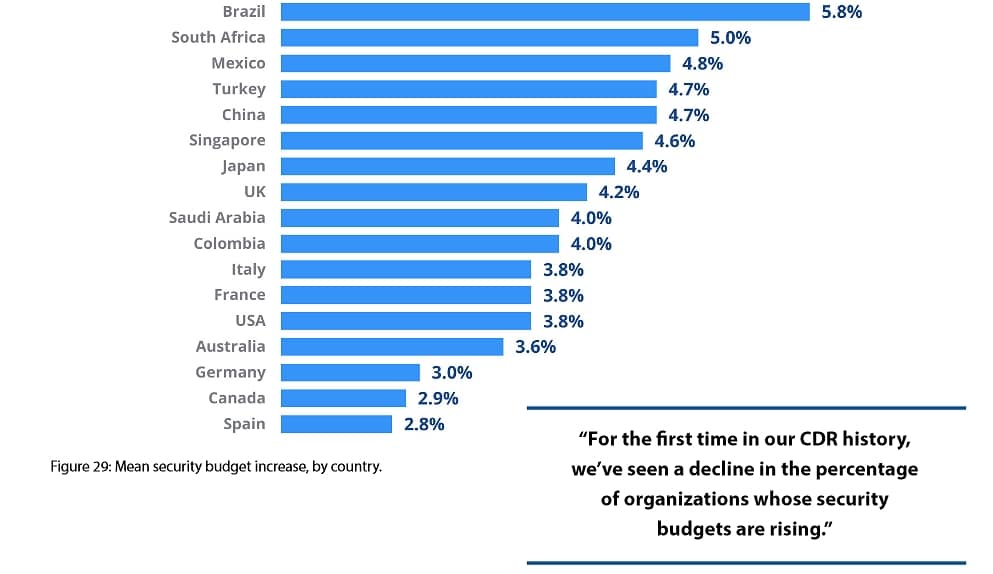
3. US organizations upped security budgets by almost 4% in 2021
According to the CDR, US organizations increase their security budgets by 3.8% in 2021. This is considerably lower than in the previous 12 months, when they upped their budget by 4.9 percent. In 2021, US firms spent an average of 13.7 percent of their IT budgets on security.
4. Nearly 89% of US businesses prefer using security products that utilize machine learning and AI
An interesting area the CDR focuses on is the preference firms have for security products that draw on advanced technologies such as AI and machine learning. It found that 89 percent of American companies surveyed had a moderate to strong preference for these technologies. This was about average, with Saudi firms (98 percent) having the strongest interest and German companies (71.6 percent) having the least.
5. The US endures the largest portion of ransomware Trojan attacks
A Kaspersky study of mobile malware revealed that the US was by far the most attacked country by mobile ransomware Trojans. It had a 2.25 per cent share of attacked users compared to the next highest Kazakhstan (0.77 percent), followed by Iran (0.35 percent), and China (0.21 percent).
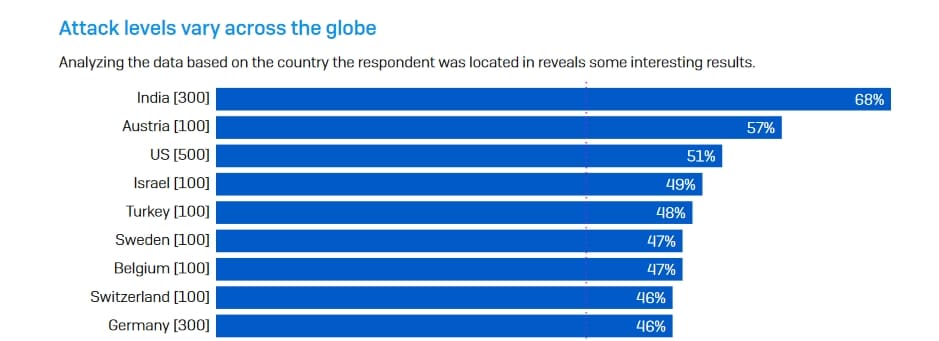
6. 59% of organizations were hit by ransomware
The Sophos State of Ransomware Report 2020 provides a wealth of information about this type of malware which is wreaking havoc on individuals and businesses alike. In the US, 59 percent of organizations were hit by a ransomware attack in 2020. In a similar report published in 2021, that number had dropped to 51% of organizations.
This made it the second most attacked country ( up from 6th the year before) behind India (68 percent) and Austria 57%.
7. Attacks were stopped before data was encrypted in 25% of cases
In 2020, Sophos found that around one-quarter of attacks were blocked before the malware managed to encrypt data. This is good news for those businesses but not so for the other 75 percent. Companies in Turkey, Spain, and Italy fared better, thwarting 51 percent, 44 percent, and 38 percent of attacks respectively.
In its 2021 report, Sophos found that cybercriminals had been nearly 20% less successful at encrypting data during ransomware attacks. An increase in attacks being thwarted before data was encrypted was also noted. This appears to prove that the security being put in place to spot and prevent ransomware attacks is beginning to bear fruit.
8. One quarter of US organizations paid the ransom
So what about ransom payments? 25% of US firms that suffered a ransomware attack paid the amount demanded. This number was just above the global average but was more than six times higher than the figure in Spain (four percent), where firms are the least likely to pay up. In 2021, global averages revealed that companies were choosing to pay ransoms around 6% more than the year before.
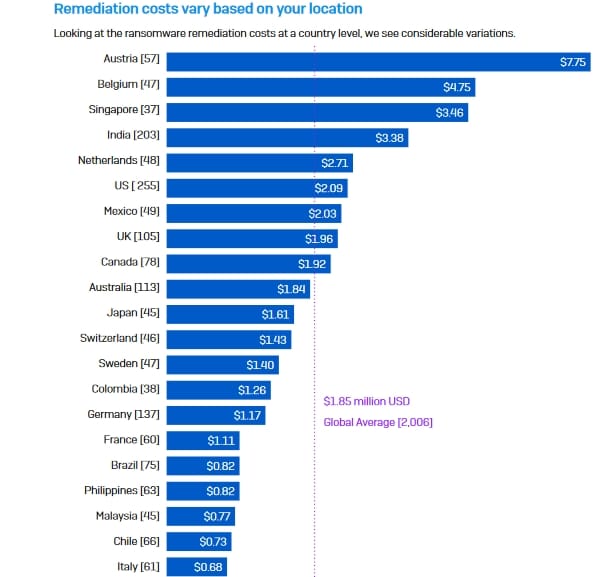
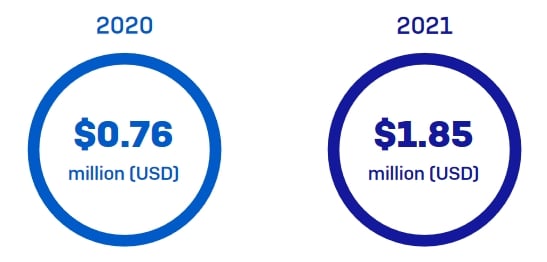
9. US companies paid an average of $620,000 in remediation costs
Ransomware attacks represent a range of other costs to businesses. In 2020, Sophos revealed that the average remediation cost for a ransomware attack was $761,000. In 2021, this sum went stratospheric rising more than 50% to 1.85 million.
The cost of ransomware attacks in the US was actually above this global average at $2.09 million. Austrian companies saw the highest costs, surpassing $7.7 million, and the Czech Republic saw the lowest at around $370,000.
10. 9 in 10 organizations have cyber security insurance
One more area Sophos reported on was how many companies in each region have cyber security insurance. It discovered that 90 percent of US businesses hold a cyber insurance policy, putting the country in the top five on the list. Of those, three quarters (75 percent) have ransomware covered in their policy.
11. Almost 12% of users tried to open a phishing link in 2020
Another Kaspersky study reveals the habits of users with respect to phishing emails. It found that 11.82 percent of users in the US attempted to open at least one phishing link in 2020. Brazilians (19.94 percent) were most likely to have tried opening a phishing link.
In Q2 of 2021, another study found that corporate accounts were a primary target for hackers who sought to use fake notifications from popular cloud services, such as invitations to Microsoft Teams meetings, to forward users to phishing pages that lift their corporate credentials.
12. The US was the third-largest source of spam
The same study reveals the major sources of spam. Russia was the worst offender, with 21.27 percent of spam originating in the country. Germany (10.97 percent) was in second and the US (10.47 percent) in third.
13. The US tops the list of the most COVID-related malicious file detections
According to statistics from McAfee, there have been a total of more than 16 million COVID-19 related malicious file detections since December 2020. Almost 1.09 million of these were observed in the US. A fairly close second is Spain with 786,000 million detections, and in third is South Africa with around 731,000.
These stats are actually an improvement over the 12 months before, when the US had over 2 million malicious file detections in a 12 month period.
14. The US ranks 45th out of 75 for cybersecurity performance
A Comparitech study analyzed the cyber health of 75 countries around the world. It used over a dozen criteria to come up with an overall score for each country. The US scored 19.69 (lower is better) putting it in 45th place overall. The top scorer was Denmark with 3.56 and the last on the list was Tajikistan with 35.54.
15. The US has the highest portion of firms qualifying as cyber experts
The Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2021 refers to each organization as expert, intermediate, or novice in relation to cyber security. It found that the US has the highest proportion (25 percent) of firms that qualify as cyber experts. It also found that the country has the lowest portion (27 percent) of companies that were considered cyber novices.
16. 18% of firms had to pay a substantial fine as a result of a breach
Of the US firms participating in the Hiscox study, a large portion (18 percent) said they had to pay a substantial fine as the result of a breach. This was well over the global average of 11 percent.
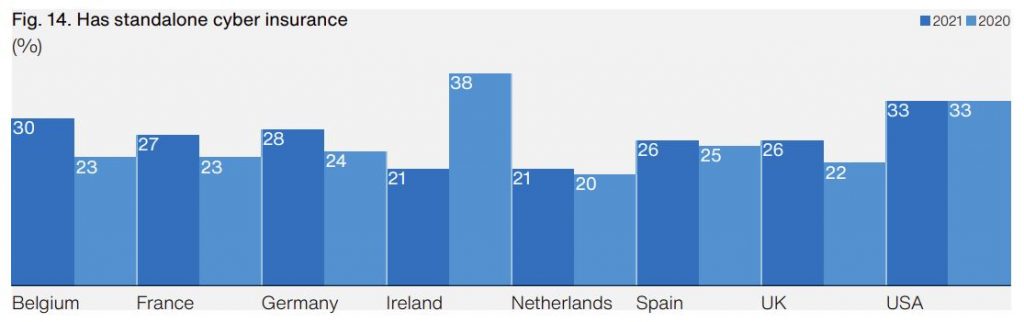
17. 33% have standalone cyber insurance
Hiscox also looked at cyber insurance policies and found that around one third of US firms hold a standalone cyber insurance policy. This number was unchanged from 2020.
18. The US is the third most affected country by stalkerware
A 2020 Kaspersky study into stalkerware gathered data about the number of incidents in regions across the globe. It found that Russia had the highest number (12,389) of affected users. This was followed by Brazil (6,523) and the US (4,745) was the third most affected by stalkerware.
In 2021, a study by Norton reported that stalkerware was massively on the rise, with 250,000 devices found to be compromised with over 6,000 stalkerware variants in May of 2021 alone. According to the study, despite the high prevalence of stalkerware 86% of adults are unaware of its existence or the danger that someone in their household may be snooping on them.
19. 75% of US organizations experienced phishing attacks
The Proofpoint 2021 State of the Phish reveals that three-quarters of US organizations dealt with a successful phishing attempt in 2020. This was 30 percent above the global average and represented a 14 percent increase compared to 2019. 35 percent of those affected experienced immediate financial loss, twice the global average.
20. US firms faced many and varied social engineering attacks
Proofpoint’s study of social engineering attacks went beyond email and into areas such as smishing and fishing in the US. It found that 81 percent of US firms had faced smishing attacks in 2020 and 77 percent had experienced vishing schemes. What’s more, a surprising 80 percent had dealt with weaponized USB drives.
21. Only 52% of US workers know what phishing is
Proofpoint asked respondents about the definitions of various terms including phishing, ransomware, malware, and smishing. Only just over half (52 percent) knew the correct definition for the term phishing, although this was up slightly compared to 49 percent in 2019. The global average was 63 percent. The UK performed the best with 69 percent knowing the correct definition.
22. 54% know the definition of malware
Again, only around half of US respondents knew the definition of the term malware. This was well below the global average of 65 percent. In its 2020 study, Proofpoint found that 30 percent of US workers think malware is a type of wifi-boosting hardware.
23. 75% give family members and friends access to work-issued devices
Around three quarters of US respondents to the Proofpoint study admitted that they allow friends and family members to access their work-issued device for various tasks such as checking emails, reading news, using social media, and shopping online.
24. 28% of US businesses use MFA
The 3rd Annual Global Password Security Report by LastPass studied how employees use passwords and other authentication methods. It found that in the US, 28 percent of businesses use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). This is around average, with Denmark (46 percent) heading the list and Italy (20 percent) at the bottom.
25. The average employee has 75 passwords
LastPass also asked how many passwords each employee uses and discovered that US employees generally deal with around 75 passwords. Again, this was about average. Employees in Belgium have to manage 115 passwords and those in Sweden, just 50.
26. American company Google was issued the largest GDPR fine to date
Although the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU-governed regulation, it still impacts companies across the pond, and indeed all over the globe. Any company that deals with the data of EU citizens must adhere to the regulations. And it was made very clear that US companies would not be immune when the largest GDPR fine to date was issued to US-based firm Google. In January 2019, the company was ordered to pay €50,000,000 for not observing principles around transparency, sufficiency of information, and the presence of legal basis.
27. The US had the highest data breach costs averaging $9.05 million
The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2021 provides details about data breaches including the time taken to identify them and the costs involved. In the US the average cost of a data breach rose from $8.64 million per incident in 2020 to $9.05 million in 2021. This is by far the highest, with the Middle East in second place with $6.93 million, followed by Canada with an average cost of $5.4 million. World averages were up 10% year on year.
28. 24% of breaches are the result of human error
IBM tells us the cause behind breaches and found that almost one-quarter (24 percent) are caused by human error. That said, the largest cause of breaches is malicious attacks, behind 54 percent of incidents. A further 22 percent are caused by system glitches.
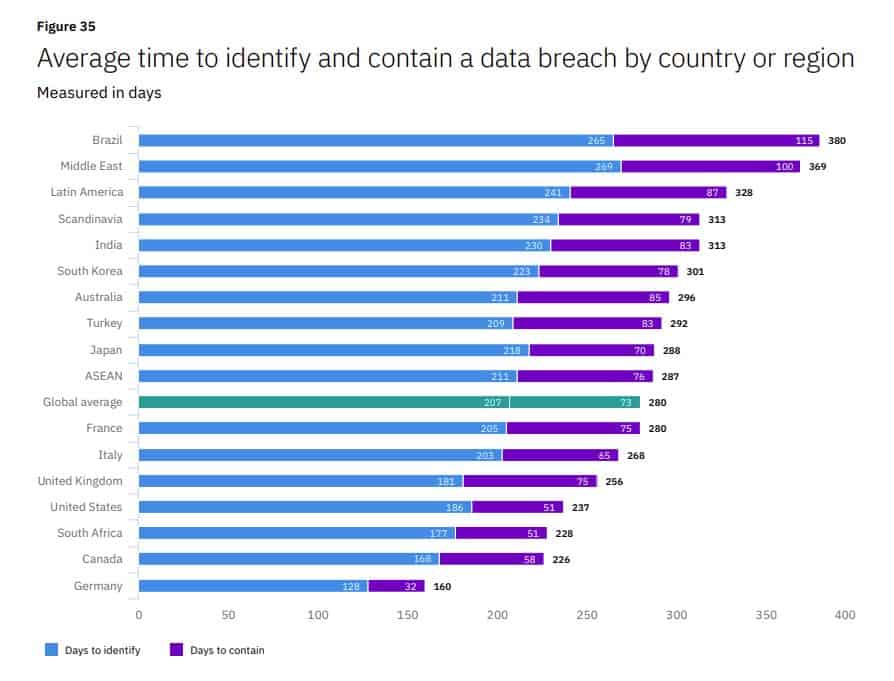
29. It takes US companies an average of 186 days to identify a data breach
Wondering how long it takes to identify and contain a breach? You may be surprised to learn that the average identification time is 207 days and time to containment is 73 days. US firms do a little better than this, taking an average of 186 days to identify and 51 days to contain a breach.
30. The IC3 received over 790,000 complaints in 2020
The Internet Crime Report 2020 from the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) reveals the number of internet crime complaints received each year since 2016. The 2020 figure was 791,790, way up over 2019’s number of 467,361. The large majority of reported crimes involved phishing or similar. The losses associated with the 2020 reports totaled $4.2 billion. Since 2016, there have been a total of 2.2 million complaints resulting in losses of $13.3 billion.
31. More than 70 top cyber criminals conspired against the US in 2020
The FBI’s most-wanted cybercriminals list highlighted 70 of the most dangerous groups and individuals seeking to carry out damaging crimes in 2020. These crimes include espionage, identity theft, wire fraud, computer intrusions, and more.
32. There was a shortage of 377,000 IT security jobs in 2021
The Cybersecurity Workforce Study 2021 from ISC reported a staffing gap of 377,000 jobs in the United States alone in 2021. Globally, the shortage in IT Security roles reached 2.1 million.
33. Supply chain ransomware was the biggest threat in 2021
Tech Target reports that ransomware was the most significant cybersecurity challenge in 2021. In May 2021, the East Coast of the US was impacted when a considerable ransomware attack hit its Colonial Pipeline. Experts believed the attack was formed using a compromised password from the dark web. While the attack was on the billing systems as opposed to the oil pumps, the supplier decided to shut down the pipeline to ensure no other vulnerabilities were taken advantage of by the attackers. The ransom of $4.4 million was paid to the hacking group, who supplied a tool to restore the systems to their original state, though the process took several hours to complete.
34. DDoS Attacks in the US increased by 7% in 2021
According to Netscout’s 2021 Threat Intelligence Report, DDoS attacks grew by 11% in the first half of 2021 versus the first half of 2020. DDoS attacks were the most significant in the United States in Q1 2021, contributing to 7% of the reported attacks.
35. The US continues to host the most botnet-controlled servers
A report from PurpleSec identified the United States as the central host of botnet control servers. 36% of the hosted botnets were in America, while 24% were hosted in unidentified locations.
See also:
- Malware statistics in 2022
- 300+ Terrifying cyber crime statistics
- Identity theft statistics (2022)
- 2022 Phishing statistics
- 50+ Shocking ransomware statistics
L’article 30+ US cyber security and cyber crime statistics (2022) est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.



0 Commentaires