
Over the last three years, US businesses that specialize in manufacturing and utilities have suffered 562 data breaches affecting nearly 91 million records. Based on the average cost per breached record (as reported by IBM each year), we estimate these breaches may have cost these businesses more than $14.7 billion. In 2022 alone, 136 data breaches are estimated to have cost more than $6 billion.
In 2021, manufacturing and utility data breaches reached an all-time high of 252 breaches–a 45 percent increase in the number of breaches that occurred in 2020 (174). In 2022, the number of breaches decreased significantly (by 46 percent) to just 136 breaches, however, estimated cost figures remained high and the average number of records involved grew exponentially.
2.4 million records were breached in 2020. This skyrocketed to nearly 50.8 million records in 2021 and a further 37.7 million in 2022. The vast majority of these impacted records came from two data breaches in the same company–T-Mobile–where 47.8 million and 37 million records were breached respectively.
When we look at the average number of records lost per breach, for 2020 it was just 20,453. This increased by more than 10 times in 2021 to 283,564 before rising even further to 433,319 in 2022. This shows that despite there not being as many breaches in 2022, the data lost during each one has grown significantly. Likewise, the true extent of breaches often isn’t felt for months, if not years, so the average number of records affected per breach this year could increase even further yet.
So, what are these breaches costing manufacturing companies and utilities, how have they developed over time, and what threat does 2023 pose for data breaches within these sectors?
Our team of researchers collated information on manufacturing/utility data breaches over the last three years. We searched through state data breach reports, news, press releases, and industry reports to create an extensive list of breaches that have affected businesses across the United States.
Key findings from 2022
- 136 manufacturing/utility businesses suffered data breaches
- 37,698,781 records were affected because of these breaches
- The cost of these affected records was more than $6.18 million
- The average number of records breached in 2022 was 433,319 per breach (a 53 percent increase on 2021’s average records breached–283,564)
- California had the most breaches overall (17), followed by Ohio (12), and New York (10)
- Washington had the highest number of records affected (37 million), the vast majority coming from the November 2022 T-Mobile data breach
- California and Colorado were the only two other states that reported more than 100,000 records breached: 201,977 and 200,000, respectively
- The most common type of breach was hacking with 62 entities breached followed by ransomware with 50
The worst-hit states for manufacturing & utilities data breaches in 2022
California reported the highest number of data breaches in 2022 with 17 in total. Ohio reported 12 breaches, and New York reported 10. They were closely followed by Illinois and Wisconsin with 8 each and Washington and Virginia with 7 each. There were 11 states that did not suffer a manufacturing/utility data breach in 2022 (Alaska, Delaware, the District of Columbia, Hawaii, Idaho, Kansas, Montana, New Mexico, North Dakota, West Virginia, and Wyoming).
The state with the highest number of records breached in 2022 was Washington with more than 37 million. The vast majority of these came from the T-Mobile breach that occurred in November 2022 and exposed 37 million customer records after a hacking incident. However, it is important to note that, while T-Mobile’s US head office is based in Washington, the people affected by the breach are nationwide. This is likely the same for a number of other companies, too. However, each breach and the number of records affected has been assigned to the state where the organization’s head office is located.
California had the second-highest number of records breached in 2022 with nearly 202,000. This amount of records came from two ransomware attacks that occurred in 2022: Nvidia in February (71,335 breached records) and Omnicell, Inc. in May (126,000 breached records). Colorado was the only other state to exceed the 100,000 mark for breached figures, due to a breach at Colorado Springs Utilities (200,000 records).
Manufacturing & utility data breaches and records affected by year and state
| TOTAL | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Total # of Breaches | Total # of Records | # of Breaches | # of Records Affected | # of Breaches | # of Records Affected | # of Breaches | # of Records Affected |
| Alabama | 9 | 50,241 | 5 | 45,146 | 3 | 4,332 | 1 | 763 |
| Alaska | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Arizona | 6 | 33,123 | 2 | 4,131 | 3 | 28,992 | 1 | 0 |
| Arkansas | 4 | 157,355 | 3 | 155,455 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1,900 |
| California | 69 | 413,235 | 21 | 142,886 | 31 | 68,372 | 17 | 201,977 |
| Colorado | 7 | 210,117 | 2 | 4,982 | 3 | 5,135 | 2 | 200,000 |
| Connecticut | 10 | 7,090 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 5,669 | 3 | 1,421 |
| Delaware | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| District of Columbia | 1 | 8,500 | 1 | 8,500 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Florida | 19 | 492,994 | 11 | 38,460 | 6 | 454,534 | 2 | 0 |
| Georgia | 15 | 177,244 | 3 | 96,127 | 7 | 28,649 | 5 | 52,468 |
| Hawaii | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Idaho | 2 | 45,673 | 2 | 45,673 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Illinois | 30 | 186,327 | 10 | 22,454 | 12 | 109,798 | 8 | 54,075 |
| Indiana | 9 | 13,689 | 3 | 4,909 | 5 | 8,288 | 1 | 492 |
| Iowa | 9 | 52,481 | 2 | 5,412 | 4 | 6,052 | 3 | 41,017 |
| Kansas | 5 | 870,861 | 1 | 857,611 | 4 | 13,250 | 0 | 0 |
| Kentucky | 5 | 14,899 | 2 | 530 | 2 | 14,114 | 1 | 255 |
| Louisiana | 5 | 24,196 | 2 | 2,073 | 2 | 22,004 | 1 | 119 |
| Maine | 4 | 786 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 130 | 2 | 656 |
| Maryland | 7 | 124,332 | 1 | 102,800 | 4 | 19,613 | 2 | 1,919 |
| Massachusetts | 35 | 52,785 | 10 | 15,824 | 19 | 32,136 | 6 | 4,825 |
| Michigan | 15 | 30,553 | 8 | 16,861 | 5 | 12,891 | 2 | 801 |
| Minnesota | 14 | 97,757 | 6 | 43,229 | 5 | 51,587 | 3 | 2,941 |
| Mississippi | 3 | 9,375 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 8,860 | 1 | 515 |
| Missouri | 12 | 12,307 | 4 | 5,403 | 7 | 5,561 | 1 | 1,343 |
| Montana | 1 | 2,976 | 1 | 2,976 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nebraska | 5 | 6,920 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2,937 | 2 | 3,983 |
| Nevada | 5 | 1,481,280 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1,481,280 | 1 | 0 |
| New Hampshire | 9 | 3,824 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3,761 | 3 | 63 |
| New Jersey | 17 | 84,829 | 5 | 7,636 | 10 | 77,193 | 2 | 0 |
| New Mexico | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| New York | 33 | 283,544 | 9 | 263,871 | 14 | 16,649 | 10 | 3,024 |
| North Carolina | 11 | 12,444 | 3 | 7,432 | 7 | 5,012 | 1 | 0 |
| North Dakota | 1 | 12,212 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12,212 | 0 | 0 |
| Ohio | 26 | 60,956 | 4 | 8,262 | 10 | 39,895 | 12 | 12,799 |
| Oklahoma | 10 | 55,387 | 2 | 25,372 | 7 | 30,015 | 1 | 0 |
| Oregon | 10 | 58,832 | 3 | 44,735 | 4 | 8,513 | 3 | 5,584 |
| Pennsylvania | 17 | 68,204 | 7 | 49,876 | 9 | 17,581 | 1 | 747 |
| Rhode Island | 3 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 2 | 0 |
| South Carolina | 5 | 34,126 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8,099 | 2 | 26,027 |
| South Dakota | 3 | 6,064 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6,064 |
| Tennessee | 6 | 1,551 | 2 | 451 | 3 | 1,100 | 1 | 0 |
| Texas | 32 | 593,954 | 13 | 288,392 | 15 | 301,267 | 4 | 4,295 |
| Utah | 6 | 6,493 | 3 | 4,921 | 2 | 897 | 1 | 675 |
| Vermont | 3 | 10,542 | 1 | 10,341 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 201 |
| Virginia | 13 | 26,740 | 2 | 6,262 | 4 | 14,300 | 7 | 6,178 |
| Washington | 30 | 84,862,209 | 7 | 30,796 | 16 | 47,827,804 | 7 | 37,003,609 |
| West Virginia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Wisconsin | 19 | 111,132 | 5 | 43,685 | 6 | 9,402 | 8 | 58,045 |
| Wyoming | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTALS | 562 | 90,870,154 | 174 | 2,413,474 | 252 | 50,757,899 | 136 | 37,698,781 |
The cost of manufacturing & utility data breaches by year
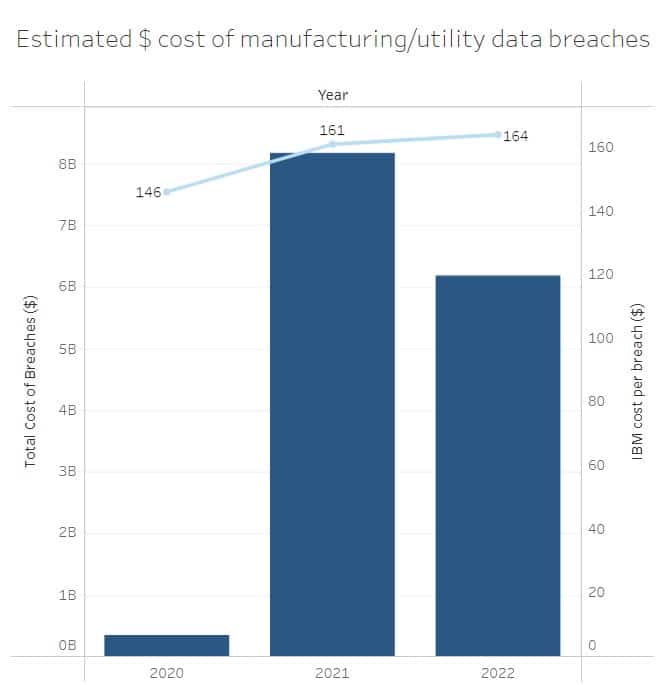
According to IBM, the average cost per record involved in a breach in 2022 was $162–a slight increase on 2021’s cost of $161. 2022’s figure is the highest IBM has ever recorded and using these figures we have been able to estimate how much these breaches have cost manufacturing/utility businesses.
From 2020 to 2022, the total cost of these types of data breaches amounted to an estimated $14.7 billion.
In the last 2 years, the estimated cost of these breaches has gone through the roof– in 2020 the estimated cost of breaches was $352.4 million. This increased by more than 23 times to reach a massive $8.17 billion in 2021. Last year, we did see a small decline (24 percent) to $6.18 billion, but, as mentioned previously, with the discovery/reporting of more breaches in the coming months, this will likely rise.
Equally, while figures are already extraordinarily high, the true costs are likely much higher. This is not just because of all of the other costs involved in a data breach (e.g. recovery costs and ransom payments) but because some figures are unavailable for the number of records involved in breaches.
The top 5 biggest manufacturing/utility data breaches in 2022
- T-Mobile – 37 million records: Hackers were able to access T-Mobile’s customers’ names, addresses, dates of birth, and certain details about their phone plans. T-Mobile found no evidence that malicious actors gained access to the company’s systems or network and all malicious activity was stopped after just one day.
- Colorado Springs Utilities – 200,000 records: Customer data stored by one of Colorado Springs’ subcontractors was accessed by an unauthorized party.
- Omnicell, Inc – 126,000 records: Omnicell, Inc. suffered a ransomware attack in May 2022, which impacted internal IT systems and in turn exposed personal information.
- Nvidia – 71,335 records: Nvidia (the largest microchip company in America) suffered a ransomware attack and experienced a 2-day outage due to the LAPSUS$ ransomware gang that threatened to release 1 TB of data.
- Century Aluminium Company – 48,320: An authorized party gained access to copies of files on the Century network. There is little known information about this breach.
Manufacturing & utility data breaches and records affected by month and year
As we’ve mentioned above, 2021 was the biggest year for data breaches in manufacturing/utility companies, accounting for 45 percent (252) of all breaches in the last three years. 2022, however, saw the highest average number of records being breached. This suggests hackers are seeking out companies with troves of data to cause maximum disruption through fewer attacks. By stealing a vast amount of data, it increases their chances of a “reward” whether that be via ransom payments to destroy the data or by selling the data on the dark web.
2022
- Total # of breaches – 136
- Total # of records affected – 37,698,781
- Average # of records affected – 433,319
- Total cost of breaches – $6,182,600,084
2021
- Total # of breaches – 252
- Total # of records affected – 50,757,899
- Average # of records affected – 283,564
- Total cost of breaches – $8,172,021,739
2020
- Total # of breaches – 174
- Total # of records affected – 2,413,474
- Average # of records affected – 20,453
- Total cost of breaches – $352,367,204
Manufacturing & utility data breach types
Since 2020, the breach category that has affected the most companies was hacking with 237 breaches, accounting for 42 percent of the total. Ransomware attacks were also prolific, accounting for 36 percent of all breaches with 204 attacks overall. There were also 32 insider data breaches (e.g. theft by an employee or a hacking incident via a third-party software provider) and 10 inadvertent disclosure breaches. Some breaches remain unknown (78), with certain information still unavailable.
Above we have already acknowledged the two largest data breaches with the highest number of records affected (T-Mobile), below are some other major data breaches across the different categories.
- 200 Networks, LLC (Feb 2021, DISC) – 1,481,280 records in a database of robocall logs were publicly accessible after researchers discovered them publicly exposed with no password protection.
- USA Waste-Mangement Resources, LLC (Jan 2021, HACK) – An unauthorized actor entered WM’s environment and accessed files, removing a number of them. 277,000 records were potentially affected.
- Direct Energy LP (Nov 2020, RANS) – 249,669 records were breached during a ransomware attack.
- Wilson’s Gun Shop (third-party Freestyle Software, Inc.) (Sep 2020, INSD) – A third-party software company (Freestyle software) discovered that malware had been downloaded onto a server that could have impacted 113,497 records at Wilson’s Gun Shop.
How is 2023 looking for manufacturing & utilities data breaches?
As we have already seen, hackers have become much more targeted in their approach with a huge shift to breaching “big-ticket” companies in possession of large data sets. Our recent report on ransomware found this same trend.
T-Mobile’s latest breach is also a prime example of the types of hacks being carried out and should serve as a stark warning that our data remains incredibly vulnerable–even after a company has already suffered a large-scale breach. T-Mobile only recently came to a $550 million settlement agreement for its 2021 breach which saw 48 million customer records being posted to the dark web. To have suffered another massive breach within less than two years is a key indicator that no organization, no matter the size or cybersecurity budget, is safe.
Utility and manufacturing companies are targeted by both cybercriminals looking for low-hanging fruit as well as sophisticated state-sponsored attackers. A successful attack against these companies can cause widespread outages and supply chain issues, not to mention putting customer privacy at risk. Sophisticated or not, most successful attacks start by exploiting human vulnerabilities, not software vulnerabilities, and that trend isn’t going to change in 2023.
Methodology
Using state reports, news, press releases, and industry reports, we have collated all of the records of data breaches that have occurred in companies that specialize in manufacturing and utilities– including two subcategories– healthcare manufacturing and food manufacturing.
Our research found 562 manufacturing and utility data breaches in total from 2020 to 2022. Out of these, we went on to find the number of records affected for each breach (if the data was available). Using this information, we could then use figures provided by IBM to make estimates as to how much these breaches are costing businesses. IBM’s yearly figure (e.g. $162 for 2022) was added to the number of records affected to create an estimated total amount lost.
For a full list of sources, please request access here.
Researcher: Charlotte Bond
L’article US manufacturing & utility businesses leaked nearly 38 million records in 136 data breaches in 2022 est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.
0 Commentaires