One of the best ways of securing a network is by making sure all versions of the application and operating system software are running their latest versions and that all their vulnerabilities have been patched. Hackers won’t be able to run amok on a network if all exploitable weaknesses have been patched.
And the best way of achieving this level of security is with the help of some of the seven best-automated patch management tools we will soon be looking into later in this post.
Here is our list of the seven best automated patch management tools:
- SolarWinds Patch Manager FREE TRIAL A patch management tool from a leader in the industry that streamlines patching processes for all devices, virtual machines, and other connected endpoints; it comes with pre-built and pre-tested patches that can be deployed to any device, even when it is offline. Get a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus All-rounded automatic patching platform for Windows, macOS, and Linux and over 250 third-party applications; allows for customizable deployments for services packs, roles, antivirus definitions, and patches.
- Atera Remote Monitoring and Management An easy-to-use automatic patching tool that integrates well with third-party solutions to cover any network architecture; for example, it works directly with Microsoft’s Knowledge Base (KB) for a quicker, more exact patching process.
- NinjaRMM Best tool for administrators of mostly remote or cloud architecture; features include automatic, scheduled, and targeted patching as well as scripting and antivirus management capabilities to ensure endpoint security.
- Avast Business Patch Management This tool is from a significant, well-tested antivirus maker; the patch management solution is quick and light and can send customized patches to devices regardless of where in the network they may lie: remote, mobile, behind a firewall, or even asleep.
- Quest KACE Systems Management Offers automatic patch management and deployment of many patches; it can be deployed locally or in the cloud and still manages patches in complex and heterogeneous network architectures with ease.
- Kaseya VSA A remote endpoint management tool for networks of all sizes; it manages patches on Windows and Mac operating systems without affecting the end users’ work, network bandwidth, or device performance.
What to look for in a great automated patch management tool
Looking for the best-automated patch management tools involves finding those with features or services that are unique, comprehensive enough to include whole networks, help make an administrator’s life more accessible, and their networks safer.
These features include:
- Ease of installation, ease of use – a good application is easy to install and run; the best don’t even need manual configurations or intervention as they start running straight out of the box.
- Integration level – administrators shouldn’t have to deal with conflicts or crashes when they install a new patch management tool; on the contrary, the new tool should enhance the performance of the network as well as the applications running on it.
- Versions: cloud, on-premises or hybrid – today’s computer networks are complex; the best applications should have versions that cater to any unique architecture, regardless of the complexity of the diversity of the software running on them.
- Ability to work on any platform – businesses can opt to run a potpourri of operating systems, and the new tool should be able to work on, as well as cater to, all the platforms they have.
- Patch selection – a good patch management tool should pick the correct version of a patch to fix vulnerabilities correctly; it should automatically spot the vulnerabilities and find the right patch from its directory or by downloading it from the software manufacturer’s site.
- Patch sequencing – once vulnerabilities are detected, the tool should determine which patch comes first, second, etc., to avoid collisions and crashes.
- Ability to reach as many devices as possible – the best tools can connect to all the devices on the network; in fact, they can connect to devices when they are asleep via Wake-on-LAN (WoL) and even when they are offline.
- Automation of tasks; and not just patch management – the tool should be able to manage the scheduling, selection, filtering, and patching of devices, applications, and operating systems; it should always be in a continuous monitoring mode to spot vulnerabilities as soon as they appear.
- Insightful reports – dashboards and audit reports should be clear and concise; they need to show patch statuses and alerts for unfinished jobs, for example, and that can be drilled down further into to extract as much information as possible.
- Light-footed – its digital footprint and resource consumption should be so small that it won’t affect network or endpoint performances.
- Price – free is always good, but in some cases, the cost-benefit analysis and ROI (return on investment) could make premium products more valuable and, hence, worth the investment.
And so, it is based on these criteria that we have tested and compared solutions to come up with the seven best-automated patch management tools.
The Best Automated Patch Management Tools
We will now have a detailed look at each of the seven best-automated patch management tools.
1. SolarWinds Patch Manager (FREE TRIAL)
SolarWinds is a leader in the server and network monitoring and management software solution market. Their Patch Manager is a security and patch management solution. And this, too, is one of their quality products that are popular among users.
It is the ideal tool for larger businesses with more extensive networks that cater to many connected devices.
Here are some more features:
- SolarWinds Patch Manager streamlines patch compliance and severely reduces the time spent on patching Microsoft and other third-party applications.
- It comes with pre-built and pre-tested patches for quicker and more accurate patching processes.
- It can manage patches on virtual desktops and servers and even patch offline devices; it can also inventory and organize virtual machines into groups for easier management.
- The tool increases a network’s security by extending Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) to keep updated on the latest security patches from Microsoft; administrators can efficiently deploy, manage, and view reports on both Microsoft and third-party patches.
- Apart from WSUS, it also works with Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) to further enhance capabilities in patch management, compliance, and reporting.
- Administrators can use the vulnerability management feature to discover any patch vulnerabilities in Microsoft applications.
- The installation of patches and updates can be scheduled before they are implemented, allowing for optimal, seamless patching as far as the end-users are concerned.
- Patch Manager makes it easy to perform updates across tens of thousands of servers and workstations – that is why it would be an ideal choice for mid-sized to larger businesses with proportional networks.
- The software also includes pre-built test packages that help administrators patch researching, scripting, packaging, and testing.
- The tool comes with customizable reports and dashboards, which allow administrators to track the status of patches and system updates during production, testing, and deployment stages.
- These reports can be saved and stored for later use as compliance reports during audits, for example.
The SolarWinds Patch Manager is available for a 30-day free trial.
2. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus is a comprehensive, all-rounded patching platform that offers automated patch deployment for multiple operating systems – including Windows, macOS, and Linux – and over 250 third-party applications.
Patch Manager Plus is a software solution for small, midsized, and large enterprises – size doesn’t matter. Also, administrators can go traditional with an on-premises installation or implement a cloud version for managed remote administration.
More features include:
- Patch Manager Plus’ main features are patch tracking, patch deployment, patch testing, patch compliance, and status reporting or auditing.
- It can scan and detect missing patches on any endpoint, regardless of its location – on-premises, in the cloud, or on a hybrid network.
- Once vulnerabilities have been discovered, it tests applicable patches before they are deployed to fix them – this reduces conflicts as well as the security risks themselves.
- After the tool has finished the automatic patch deployment – to both operating systems and third-party applications – the information immediately becomes available for reports and audits for better visibility, control, or subsequent actions, should it be required.
- The device types don’t matter; administrators can seamlessly deploy patches to desktops, laptops, servers, roaming devices, and virtual machines – all from a single interface.
- This patching process is backed by an extensive repository of patches for the most common business applications like Adobe, Java, WinRAR, and much more.
- Patch Manager Plus allows administrators to detect missing patches – and test them – before they are deployed.
- This is a complete automatic patch management software solution that provides enterprises with a single interface for all patch management tasks; admins can deploy service packs, assign role-based access, update antiviruses, manage server application patching as well as two-factor authentication.
- This automated patch management tool would be ideal for any enterprise size – and even if they had a high mix of operating systems.
Try ManageEngine Patch Manager FREE for 30 days.
3. Atera Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM)
Atera Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) offers complete visibility into and control of network-connected devices. Administrators and technicians using this tool find that it dramatically improves their support capabilities.
But, more importantly, it has one critical feature – a Patch Management Software – which gives the administrators complete control over their patch deployment processes and is monitored from a central location.
There’s more from this tool:
- Administrators can automate patches for operating systems, applications, and hardware; they can use robust reporting to stay on top of every agent, thus, ensuring airtight security and control while alleviating any risks.
- This tool is easy to use – administrators can simply plan the patching process’s tasks, configure preferences, and set the jobs running; this planning can be done for both servers and workstations, including applications like Java.
- The software patch management can be run for both Mac and Windows operating systems. It can also be fully automated using third-party integrations like Homebrew for Mac and Chocolatey for Windows devices.
- It has in-depth reports shared among stakeholders – from endpoint users to auditors and management, and board members.
- In fact, administrators can generate reports based on Microsoft KBs that search for patches using arguments like customer, knowledgebase, description, or agent type; they can then deploy the missing patches straight from the report.
- On the other hand, they can also see all agents that are currently up to date, those that need updating, any vulnerabilities (per agent), and a list of all missing patches – as well as the impact these faulty or missing patches may have on the overall health of the network.
- Finally, they can get feedback on deployments that weren’t successful in being handled accordingly. The necessary configuration changes – like settings or permissions – are made before the next patching schedule.
Try Atera Remote Monitoring and Management FREE for 30 days.
4. NinjaRMM
NinjaRMM is the ideal tool for administrators that need to support mostly remote clients. And, as a cloud-based remote monitoring and management tool, it also has a patch management feature for endpoints to ensure safety and compliance.
Here are some more features:
- The tool offers mass-configuration and automatic patching based on schedules or classified by categories; it doesn’t matter where the endpoint is, or even if it is on or off – as long as it is on the network (or even offline), it can be reached, managed, and monitored.
- It can automatically identify and patch vulnerabilities across the network and down to every endpoint; it is quick and can scale quickly – regardless of the size of up-scaling being done or the variety of the operating systems or applications being used.
- Dashboards and reporting make it easy to keep track of what has – or hasn’t – been done so far; they give insights into machines running Windows, Mac, or Linux operating systems.
- Apart from patching, NinjaRMM can also be used for scripting and antivirus management on the endpoints.
- In case issues are detected on the endpoints, a third-party engine keeps over 135 typical productivity applications patched – with no intervention required from the end-user.
- There is also a detailed software inventory and in-built tools to help with software deployment, removal, or blacklisting to curb vulnerabilities from unauthorized applications installed on endpoints.
- With NinjaRMM being a cloud-based tool, it means endpoints don’t have to be forced to join a domain, and no investment in a complex and costly patching server is required – administrators can reach their users’ machines anywhere in the world.
Try NinjaRMM for FREE.
5. Avast Business Patch Management
Although Avast is perhaps better known for its free cloud-based antivirus solution, it does have another popular product: Avast Business Patch Management.
This is a tool that simplifies and automates the patching process on a Windows network – and the thousands of popular third-party applications run on various versions of this operating system.
Here are more features:
- Avast BPM is a patch management solution that has proven itself in the real world; it effectively secures Windows systems – and the thousands of third-party software solutions running on them – from a single, cloud-based platform.
- A single, integrated interface lets administrators control patching processes, including patch discovery, distribution, and deployment of the patches to address particular vulnerabilities and finally reporting on the whole process.
- The tool is quick and light – it can quickly dispatch and deploy thousands of tested patches in a matter of minutes and without hogging the network’s bandwidth.
- Avast BPM can reach all devices, anywhere – they can be behind firewalls, mobile on the road, remote at a site, or even be asleep.
- It facilitates quick and accurate patching by downloading missing patches to a master agent who then seamlessly distributes them to all the connected devices that need them.
- Administrators can control these processes from an interactive dashboard that shows graphical summaries of patches that have been installed, are still missing, or have failed during deployments.
- They can even tweak their patches to create solutions with a custom vendor, product, or severity levels configured into them; automatic scans and patching can be scheduled to run automatically, at set times and dates.
- If there are issues with devices failing or other processes being affected by the recent patch deployment, administrators can simply roll back the patches and start afresh.
Try Avast Business Patch Management FREE for 30 days.
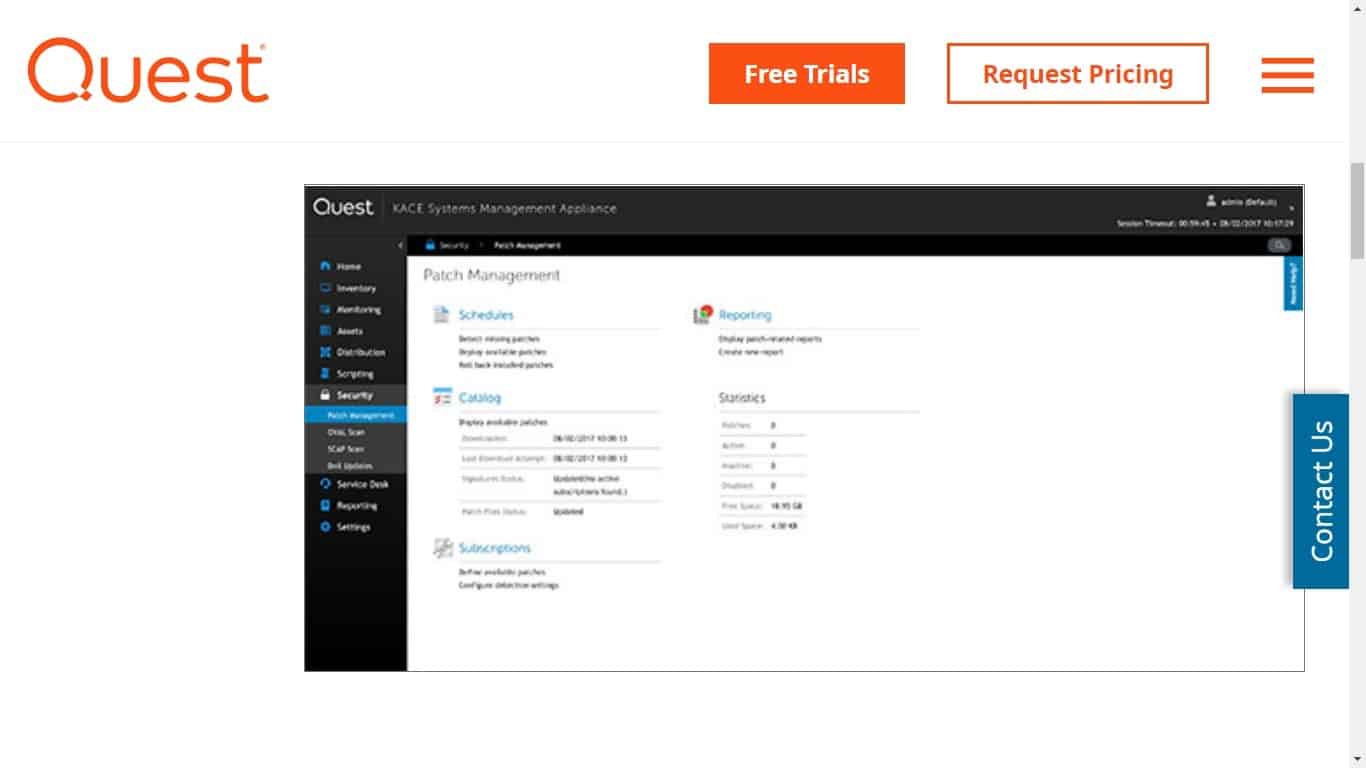
6. Quest KACE Systems Management Appliance
KACE Systems Management Appliance by Quest is a comprehensive IT systems management solution for any network-connected device. Administrators can fulfill all their remote device management needs using this solution.
This solution can also inventory all software or hardware assets and then assess them for patch management issues to spot any vulnerabilities present among them.
There’s more:
- This solution offers automatic patch management and deployment of patches from “one of the largest patch libraries in the industry.”
- It can patch both Windows and Mac platforms as well as numerous day-to-day software and applications like Adobe or Oracle Java.
- KACE can help streamline configuration and security policy enforcements by automatically deploying scripts or even manually running them if issues are encountered; these scripts can be customized to meet specific requirements.
- Patches can be dispatched to devices on the network to help with the streamlining process by blocking dangerous or unauthorized applications or gadgets while plugging vulnerabilities in mission-critical apps and operating systems.
- The tool performs periodic scans and patch assessments to spot devices where the patching has failed or where the automatic patch management isn’t performing as expected – this means there won’t be any blind spots that can then be overlooked and exploited by malicious users.
- Administrators have two options when deploying KACE – they can have it as an on-premise virtual solution or go for the remote-hosted alternative.
- This is a non-intrusive solution that lets the end-users have some control over the patching process – administrators can set deadlines to define when patches are installed. At the same time, the users themselves choose when the updates can be done or whether a reboot can occur, so their work is not interrupted at a critical moment.
- This tool works well in complex and distributed networks, and heterogeneous environments make it a good choice for larger enterprises with broader networks and a mix of devices, software solutions, and operating systems.
Try Quest KACE Systems Management Appliance FREE for 30 days.
7. Kaseya VSA
Kaseya VSA is a remote endpoint management tool that monitors servers, desktops, laptops, and printers on networks of all sizes. Remote, monitoring, remote control, process automation, antivirus or antimalware management also comes with patch management capabilities.
Delving deeper, we find:
- Administrators have real-time insights into the patch statuses of each device under their dominion – regardless if the devices are on or off the network.
- The tool automates the patching process across all platforms and smoothes out any complexities that may occur with deployments – it can be made to skip problematic patches by automating the process with scripts, for example, so that administrators can deal with them later.
- The administrators have complete control during patching – they can reject a specific patch, Microsoft Knowledge Base (KB), or block a particular update to a subnet of machines by overriding the default patch process.
- They have full software management capability for Windows and Mac operating systems and typical third-party applications used on a day-by-day basis in any working environment.
- Administrators can also monitor compliance across their networks and spot any patching anomalies in the operating system or third-party applications via custom patch reports; this monitoring process is further facilitated by aggregating the patch statuses of every device on the network, which is displayed on a single dashboard.
- And then, there is the ability to schedule scans regularly to automatically update software seamlessly without affecting the user experience (UX) on the endpoints.
Try Kaseya VSA FREE for 14 days.
Keep your software patched
Well, we have seen the best-automated patch management tools. We hope you will use at least one of them when you work towards securing your network.
We would like to hear about your experiences with these or any other automated patch management tools. Drop us a line; leave us a comment below.
L’article 7 Best Automated Patch Management Tools for 2021 est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.







0 Commentaires