ActiveBatch is a workload automation system. Simplifying this tool down to its nuts and bolts, it manages all of those batch files that you create for yourself as a systems administrator and works as a scheduler, like Cron, to launch those batch files out-of-hours and possibly on a regular cycle.
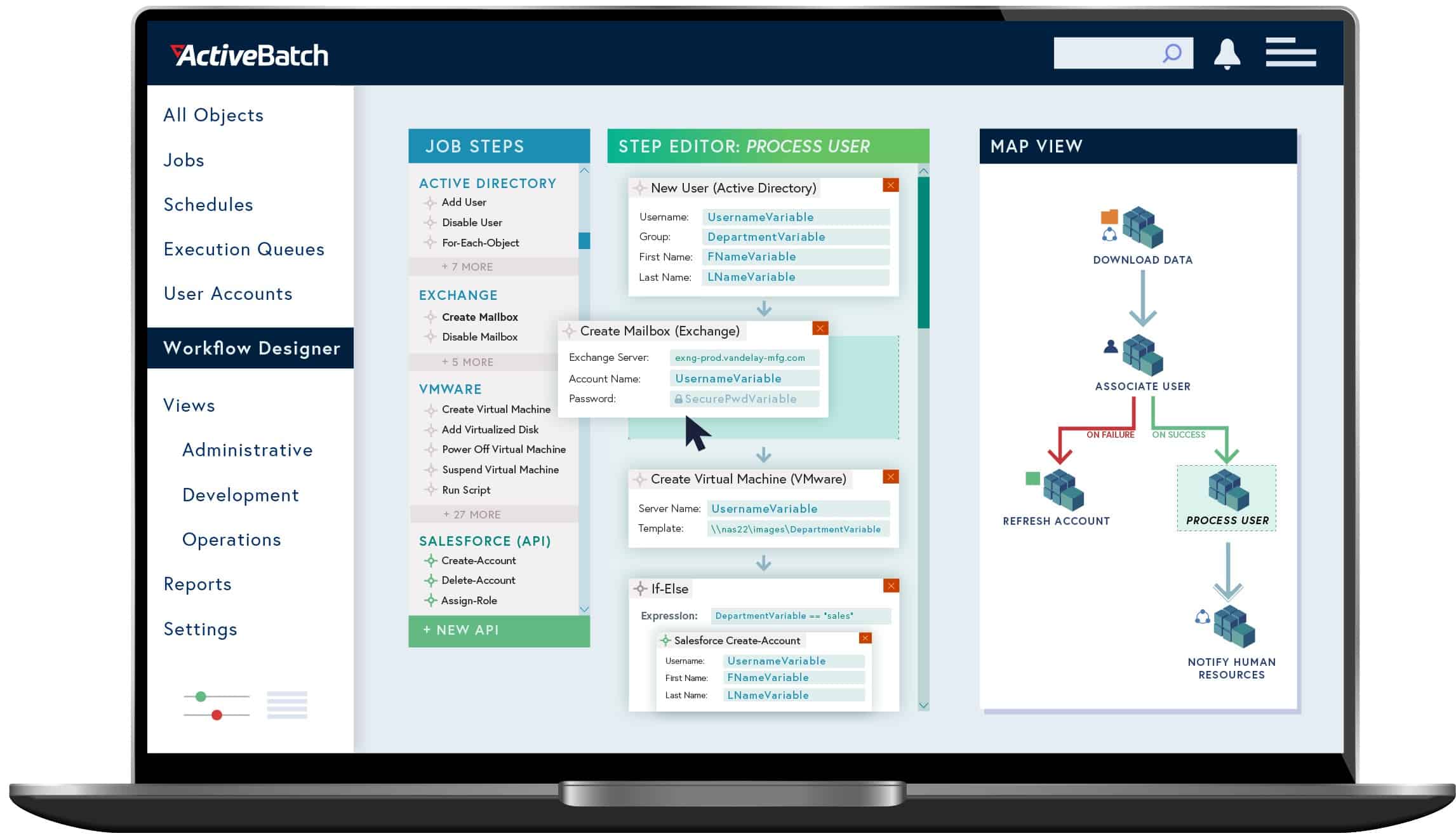
ActiveBatch offers a lot more than just a way to write your batch files as it is a sophisticated tool. It provides the opportunity to set up the actual implementation of flow diagrams. Set up processes and link them together either in parallel or in sequence. Each process can represent a series of steps, and these can be run on different devices. This cross-device capability enables you to create managed file transfer schedules that set up the transmission of files while simultaneously managing what the receiving device should do with them.
First, however. here’s our list of the six best ActiveBatch Alternatives:
- Redwood EDITOR’S CHOICE A cloud-based workload automation system that includes a graphics-based workflow creator that consists of a definition screen for each process that the system can interpret into batch steps. Access a free demo.
- ConnectWise Automate A remote monitoring and management package that includes a task automation module. This is a cloud-based system.
- BMC Control-M An applications orchestration system that coordinates data exchange between software packages that effectively builds workload automation. Available for Windows and Unix or as a hosted service.
- BMC TrueSight Automation for Servers A server management system that offers automation for many system administration maintenance tasks. Available for Windows, Linux, and Solaris.
- Ansible A data collection and management automation system that focuses on organizing security information. It runs on Linux.
- Help Systems Automate A robotic process automation system that lets you build batch jobs to complete any data processing task. Available for Windows, Windows Server, Linux, and AIX.
About ActiveBatch
ActiveBatch is a product of Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc., which was started up in 1981. The ActiveBatch system was initially called the Batch Queue Management System (BQMS).
The key features of ActiveBatch are its easy-to-use graphical user interface and its ability to set processes running on different devices, running other operating systems from within the same batch run.
How ActiveBatch works
The creation of a batch file within the ActiveBatch system is represented as a “job.” Each jo is composed of steps. You can select a step type from a menu and then enter details into the job step template. Typical steps include sending or receiving an email, transferring a file, running a program, or launching a PowerShell script.
It is possible to store jobs for later use or set them up in the ActiveBatch job scheduler. This is a timed launcher that gives you the option of running a job repeatedly on a calendar. ActiveBatch interprets each job step into instructions. Then, ActiveBatch contacts the relevant host when the job gets run and runs the files or services that the job step specifies.
Why use ActiveBatch?
ActiveBatch helps run unattended tasks out of office hours, such as purging servers of temporary files or clearing out abandoned processes. In addition, it can be used to manage log file transfers or backup processes.
ActiveBatch is also helpful for managing live system tasks, such as evaluating VM memory usage and reallocating VMs to hosts. Scripts can be triggered by events, although the main feature of ActiveBatch is its time-based scheduling system.
An advantage of running batch Jobs through ActiveBatch is that it provides a single monitor for all batch jobs running all over your system – even on cloud servers or remote sites. You, therefore, only need to visit one dashboard to get status reports on running and completed batch jobs.
Implementing ActiveBatch
The software package for ActiveBatch has two main modules, which are the console and the job scheduler. These run on Windows 10 or Windows Server 2012 and later. There is also a Web-based version of the console available, which you need to connect to your in-house Web server. This can then be accessed through any standard Web browser.
The ActiveBatch requires its back-end database. This can be SQL Server, SQL Server Azure, or Oracle.
ActiveBatch reaches out to other devices over the network, so you need to set up an execution agent on each device that ActiveBatch is expected to access.
ActiveBatch Pricing
Although it is an on-premises package, there isn’t one set price for ActiveBatch. The software package capabilities that you download are set to the number of servers that you pay for. You can get a demo of ActiveBatch to assess its suitability for your business.
The best ActiveBatch alternatives
The market for job scheduling systems has come a long way over the past few years. This field of operations is known as Workload Management, and some very high-quality systems give ActiveBatch a run for their money. However, you need to know what to look for to avoid the half-baked money-wasters in this market.
What should you look for in an ActiveBatch alternative?
We reviewed the market for workload managers like ActiveBatch and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- An easy-to-use system that includes a batch job assembler
- A scheduling system that allows periodic unattended batch job launches
- The ability to execute scripts and software on remote devices
- A central console for managing batches run anywhere in the enterprise
- An alerting mechanism for batch execution problems
- A free trial or a demo for a no-cost assessment
- Value for money represented by comprehensive functionality at a fair price
Considering these performance requirements, we looked at all of the rival systems. We assessed the ActiveBatch alternatives according to the reputation of their producers and the capabilities of each tool.
ActiveBatch implements workload automation by managing and scheduling batch files. However, this is not the only method available for task automation. The other two methods are application orchestration, which relies on integrations and APIs to run a series of processes from one application. A third method is called robotic process automation (RPA), which is a little like keystroke recorders or application macros. These record manual actions and then replay them.
The majority of ActiveBatch alternatives in our list use the batch, script, and scheduling strategy. These are very close matches for the operating methods of ActiveBatch. If you like the way ActiveBatch works and want the same system but implemented by a different software package, you will find your ideal service on this list. We have also included orchestration and RPA options. You will find options for your operating system on this list and systems running on cloud servers.
1. Redwood EDITOR’S CHOICE
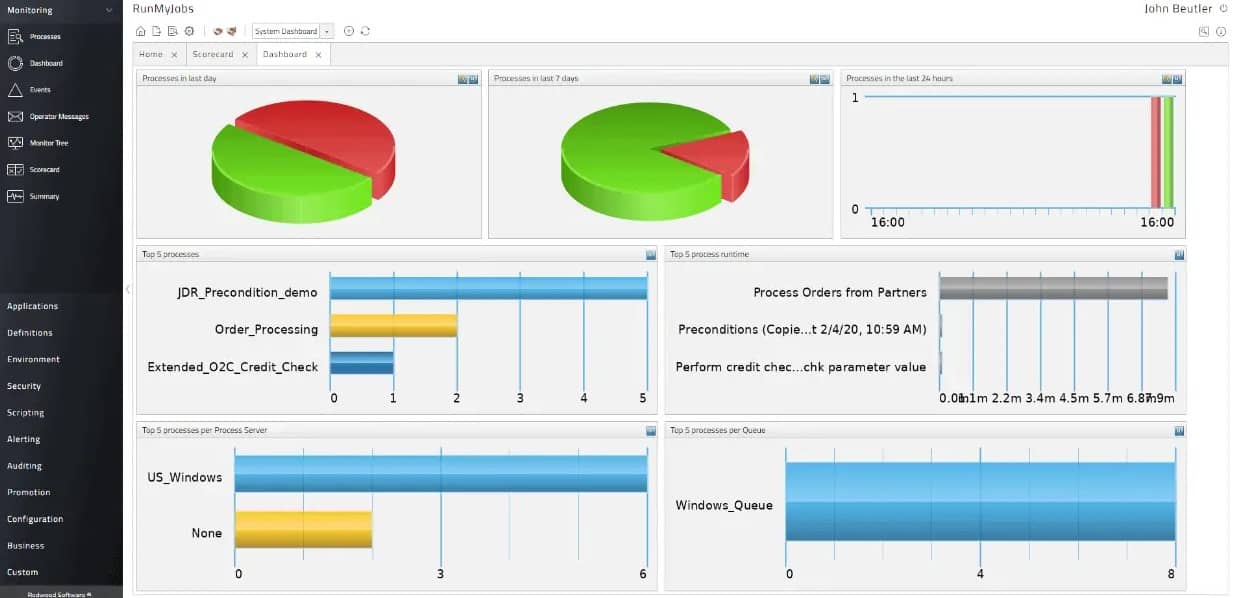
Redwood Workload Automation, previously known as RunMyJobs, is a cloud-based system for creating, managing, scheduling, and monitoring batch jobs. If you want an ActiveBatch alternative that you can subscribe to on a SaaS basis, Redwood has to be your number one choice.
Redwood includes a console and a job scheduler. You can call up a batch process template within the console and then adapt it to create your workflow. Each process in the workflow becomes a batch file. Next, you drill through to the process definition to specify the actual steps that batch jo will run. There are action types that you can select from for each step.
You can store each process and reuse it in other workflows, and you can also keep an entire workflow for later execution. The stored workflows can then be added to the scheduler. You can decide whether to run immediately, at a specific time, or repeatedly on a calendar.
The operations of Redwood are very similar to those of ActiveBatch. This system will connect to each server that the job steps are expected to run on and transfer necessary scripts and then run them. The service can control job execution on any operating system, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
Redwood is particularly useful for managing file processing across different systems by including secure file transfer steps in a batch. It can also be used for ERP management, database maintenance, and system cleanup chores.
Pros:
- An easy-to-use guided graphical batch job creator
- A scheduler to run jobs on a delayed timer or repetitively by the calendar
- Workflow storage for reuse
- A variant that specializes in ERP maintenance task management
- The ability to run jobs with steps executed on several endpoints
Cons:
- No onsite version
The pricing for Redwood is based on job execution throughput, and you can get a demo to see how it works.
EDITOR’S CHOICE
Redwood is our number one pick for an ActiveBatch alternative because it matches the ease of use of ActiveBatch and can run batches across multiple devices. In addition, redwood goes one better than ActiveBatch because, being a hosted package, you don’t bother installing it or making sure that the software is constantly updated.
Access FREE Demo: redwood.com/get-a-demo/
Operating system: Cloud-based
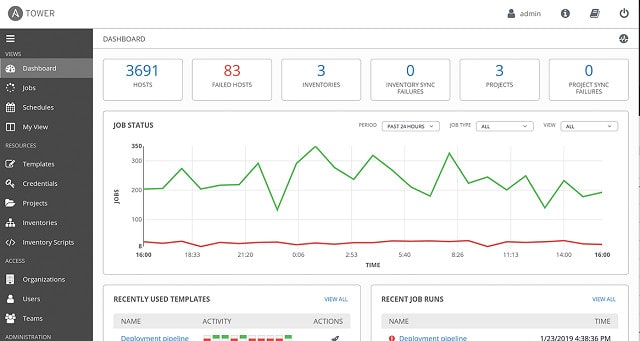
2. ConnectWise Automate
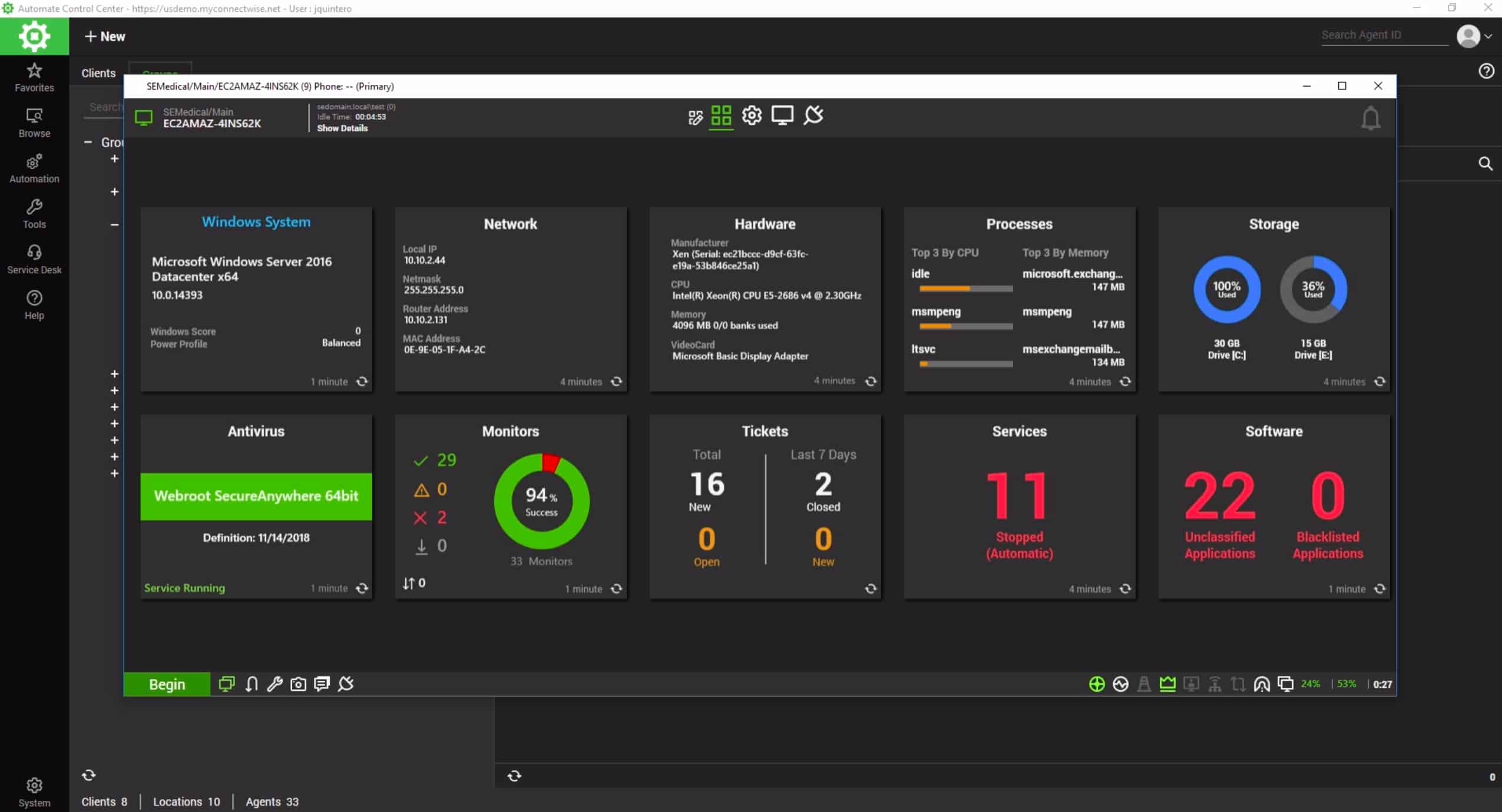
ConnectWise Automate is a remote monitoring and management (RMM) package aimed at managed service providers. However, it would also be a sound system for the IT departments of multi-site organizations.
The Automate system has many helpful features that assume system monitoring and maintenance tasks, such as device discovery and automatic software inventory scanning systems. However, this package’s automated maintenance module makes it a close match for ActiveBatch.
The maintenance services module of ConnectWise Automate is made up of a library of scripts for standard tasks. These scripts can be modified or just used off-the-shelf, and they can be linked and then added to a scheduler for triggered execution. Other automated systems within the ConnectWise package include system cleanup and batch data processing.
Some of the features in the ConnectWise system allow self-service actions by users to trigger a series of scripts within the system management modules. Password reset requests are an example of this mechanism.
All of the batch processing and scheduled tasks in ConnectWise Automate are logged, and it is possible to examine execution logs for problems and completion statuses. In addition, any issues that arise during schedule execution can be set to trigger alerts.
Pros:
- A batch job creator that is part of a wider system management server
- A job scheduler for unattended bat h execution
- The ability to run the same batch for many clients
Cons:
- Mainly written for managed service providers
ConnectWise Automate is a hosted package and multi-tenanted – it keeps the services for each client of its account holders separate. ConnectWise offers a demo system of the Automate package.
3. BMC Control-M
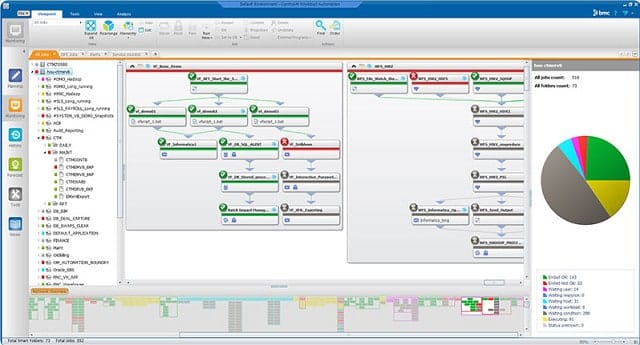
Control-M is the first of two ActiveBatch alternatives on this list that BMC provides. This is an application orchestration system that uses a different approach to task automation than the script-based strategy of ActiveBatch.
The console of Control-M includes a task workflow editor, in which you assemble a series of steps to perform. This gets interpreted down into specific actions by different applications. The service will start with a root application and then flow through commands, implementing data exchanges to ensure that all processes can be completed without human intervention.
The Control-M service includes a scheduler, so workflows can be triggered for execution out-of-hours and regularly.
Control-M helps implement business processes through orchestration or manage production systems, such as a CI/CD pipeline.
Pros:
- An easy-to-use batch creator that works with the orchestration capabilities that are built into applications
- Suitable for business process automation
- A useful tool to manage CI/CD pipelines
Cons:
- Not suitable for system administration task automation
The software for Control-M installs on Windows and Unix hosts. The system is also offered as a SaaS, hosted package as BMC Helix Control-M. In addition, BMC provides a free trial of Control-M.
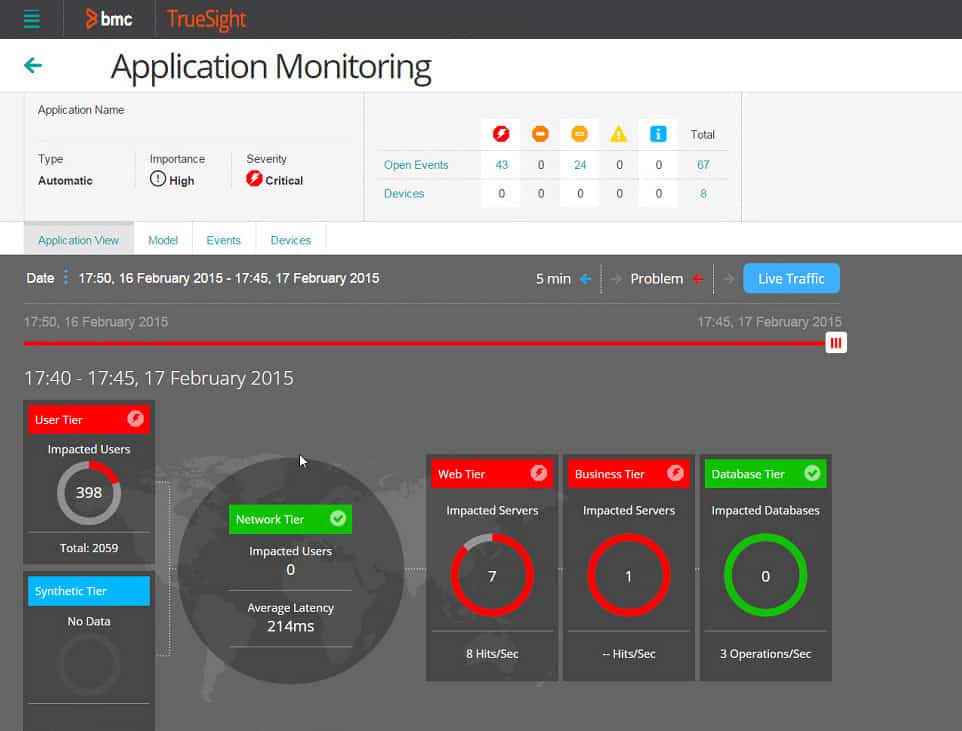
4. BMC TrueSight Automation for Servers
While Control-M automates business processes, BMC’s second entry on our list, TrueSight Automation for Servers, is aimed at systems administrators who want to automate back-end maintenance tasks. This is a much closer match for ActiveBatch. It can run the scripts you already have on file, and the console includes a batch file creator.
The purpose of the processes you set up for execution through the TrueSight scheduler is to monitor and maintain servers. Those servers can be on remote sites or cloud-based virtual servers. You can create batches to run once only or periodically on the calendar.
As well as clearing out temporary files and killing abandoned processes, this tool is a good choice for security management. It includes configuration checking and patch management for system hardening. It can also manage vulnerability scans.
Pros:
- A scheduler for local, remote, or cloud resource execution
- An easy to use batch file creator
- Includes compliance auditing features
Cons:
- Better for back-office work than front-office process automation
TrueSight can cover just about any admin task you need to perform on your servers. This includes VM management, VoIP performance monitoring, access control standardization, and data privacy compliance auditing. It can also automate backup and restore, and it can operate as a file integrity monitor.
5. Ansible
From Red Hat, Inc., Ansible offers data gathering automation that covers equipment based on your premises or the Cloud. The system is also able to manage virtualizations and containers. In addition, Ansible operates as a system monitor by accessing reporting functions that are already built into the equipment that you use.
Behind the scenes, Ansible acts like a library of those scripts that every system administrator puts together for status queries and system cleanup. The attractive front-end ties the execution of those scripts together to provide a reliable, customizable monitoring and management tool.
A typical script batch will gather data to feed into an application and then optionally launch other software packages to deal with discovered issues. Examples of tasks that Ansible can perform include virtualization management, sizing VM to host mappings, and reallocating memory and disk space whenever shortages arise.
The system is also able to monitor traffic patterns and implement traffic shaping measures. As a result, it can help improve the quality of service on VoIP connections and create better value out of network resources. In addition, the service gathers information from firewalls and other security systems and returns settings adjustments to instruct third-party systems to implement threat responses.
Pros:
- A batch management service with network management functions
- Dashboard displays track live network activity
- A well-written facility with tight security
Cons:
- No version for Windows
Ansible is available for RHEL, Ubuntu, and CentOS, but it can access services and software running on another operating system over the network. Ansible is available for a 60-day free trial.
6. Help Systems Automate
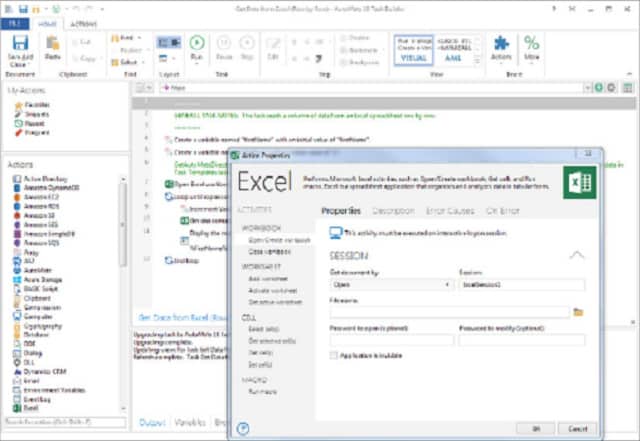
HelpSystems Automate is a robotic process automation (RPA) package. RPA involves recording your steps as you access different systems. HelpSystems produces three editions of its Automate system: Automate Desktop, Automate Plus, and Automate Ultimate.
The Desktop version focuses on business process automation. This would cover actions such as deriving data in Excel and extracting that to trigger another application, such as Word. This could be used to issue invoices or move sales data into the accounts system. The higher versions add on utilities for system administrators to perform bulk actions, such as onboarding a new employee, setting up a PC, backing up files, or moving log files securely to a store.
A significant advantage of the Automate system is that it records tasks that you are probably performing daily, so you don’t need to think about structuring a batch file.
Pros:
- A batch job builder based around a recorder
- A scheduler for unattended batch job execution
- A choice of on-device or system-wide versions
Cons:
- No hosted platform option
The Automate Desktop package installs on Windows and works with Microsoft products’ native macro recording and data exchange mechanisms. The two higher versions are available for Windows, Linux, and AIX. These versions include a recorder, which enables you to create batch jobs from any application. In addition, you can take a look at HelpSystems Automate on a 30-day free trial.
L’article 6 Best ActiveBatch Alternatives for 2021 est apparu en premier sur Comparitech.

0 Commentaires